Application of Passive Sampling to Characterise the Fish Exometabolome
- PMID: 28216558
- PMCID: PMC5372211
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo7010008
Application of Passive Sampling to Characterise the Fish Exometabolome
Abstract
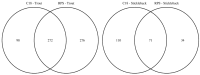
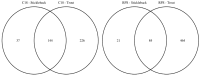
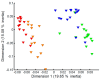
The endogenous metabolites excreted by organisms into their surrounding environment, termed the exometabolome, are important for many processes including chemical communication. In fish biology, such metabolites are also known to be informative markers of physiological status. While metabolomics is increasingly used to investigate the endogenous biochemistry of organisms, no non-targeted studies of the metabolic complexity of fish exometabolomes have been reported to date. In environmental chemistry, Chemcatcher® (Portsmouth, UK) passive samplers have been developed to sample for micro-pollutants in water. Given the importance of the fish exometabolome, we sought to evaluate the capability of Chemcatcher® samplers to capture a broad spectrum of endogenous metabolites excreted by fish and to measure these using non-targeted direct infusion mass spectrometry metabolomics. The capabilities of C18 and styrene divinylbenzene reversed-phase sulfonated (SDB-RPS) Empore™ disks for capturing non-polar and polar metabolites, respectively, were compared. Furthermore, we investigated real, complex metabolite mixtures excreted from two model fish species, rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). In total, 344 biological samples and 28 QC samples were analysed, revealing 646 and 215 m/z peaks from trout and stickleback, respectively. The measured exometabolomes were principally affected by the type of Empore™ (Hemel Hempstead, UK) disk and also by the sampling time. Many peaks were putatively annotated, including several bile acids (e.g., chenodeoxycholate, taurocholate, glycocholate, glycolithocholate, glycochenodeoxycholate, glycodeoxycholate). Collectively these observations show the ability of Chemcatcher® passive samplers to capture endogenous metabolites excreted from fish.
Keywords: DIMS; FT-ICR; bile acid; environmental metabolomics; exogenous; fish; metabolic footprinting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Williams T.D., Wu H.F., Santos E.M., Ball J., Katsiadaki I., Brown M.M., Baker P., Ortega F., Falciani F., Craft J.A., et al. Hepatic transcriptomic and metabolomic responses in the stickleback (gasterosteus aculeatus) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of dibenzanthracene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009;43:6341–6348. doi: 10.1021/es9008689. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santos E.M., Ball J.S., Williams T.D., Wu H.F., Ortega F., van Aerle R., Katsiadaki I., Falciani F., Viant M.R., Chipman J.K., et al. Identifying health impacts of exposure to copper using transcriptomics and metabolomics in a fish model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010;44:820–826. doi: 10.1021/es902558k. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Southam A.D., Lange A., Hines A., Hill E.M., Katsu Y., Iguchi T., Tyler C.R., Viant M.R. Metabolomics reveals target and off-target toxicities of a model organophosphate pesticide to roach (rutilus rutilus): Implications for biomonitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011;45:3759–3767. doi: 10.1021/es103814d. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jordan J., Zare A., Jackson L.J., Habibi H.R., Weljie A.M. Environmental contaminant mixtures at ambient concentrations invoke a metabolic stress response in goldfish not predicted from exposure to individual compounds alone. J. Proteom. Res. 2012;11:1133–1143. doi: 10.1021/pr200840b. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schock T.B., Newton S., Brenkert K., Leffler J., Bearden D.W. An nmr-based metabolomic assessment of cultured cobia health in response to dietary manipulation. Food Chem. 2012;133:90–101. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.12.077. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

