Development of a novel individualized warfarin dose algorithm based on a population pharmacokinetic model with improved prediction accuracy for Chinese patients after heart valve replacement
- PMID: 28216623
- PMCID: PMC5342672
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2016.163
Development of a novel individualized warfarin dose algorithm based on a population pharmacokinetic model with improved prediction accuracy for Chinese patients after heart valve replacement
Abstract
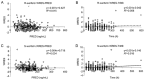
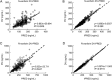
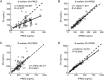
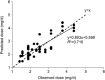
The gene-guided dosing strategy of warfarin generally leads to over-dose in patients at doses lower than 2 mg/kg, and only 50% of individual variability in daily stable doses can be explained. In this study, we developed a novel population pharmacokinetic (PK) model based on a warfarin dose algorithm for Han Chinese patients with valve replacement for improving the dose prediction accuracy, especially in patients with low doses. The individual pharmacokinetic (PK) parameter - apparent clearance of S- and R-warfarin (CLs) was obtained after establishing and validating the population PK model from 296 recruited patients with valve replacement. Then, the individual estimation of CLs, VKORC1 genotypes, the steady-state international normalized ratio (INR) values and age were used to describe the maintenance doses by multiple linear regression for 144 steady-state patients. The newly established dosing algorithm was then validated in an independent group of 42 patients and was compared with other dosing algorithms for the accuracy and precision of prediction. The final regression model developed was as follows: Dose=-0.023×AGE+1.834×VKORC1+0.952×INR+2.156×CLs (the target INR value ranges from 1.8 to 2.5). The validation of the algorithm in another group of 42 patients showed that the individual variation rate (71.6%) was higher than in the gene-guided dosing models. The over-estimation rate in patients with low doses (<2 mg/kg) was lower than the other dosing methods. This novel dosing algorithm based on a population PK model improves the predictive performance of the maintenance dose of warfarin, especially for low dose (<2 mg/d) patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Warfarin-dosing algorithm based on a population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model combined with Bayesian forecasting.Pharmacogenomics. 2009 Aug;10(8):1257-66. doi: 10.2217/pgs.09.65. Pharmacogenomics. 2009. PMID: 19663670
-
Prediction of warfarin maintenance dose in Han Chinese patients using a mechanistic model based on genetic and non-genetic factors.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 Jul;52(7):567-81. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0054-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23515956
-
Development and comparison of a new personalized warfarin stable dose prediction algorithm in Chinese patients undergoing heart valve replacement.Pharmazie. 2012 Nov;67(11):930-7. Pharmazie. 2012. PMID: 23210243
-
[Advances in warfarin's anticoagulation therapy in Chinese population after mechanical valve replacement].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 May 1;62(5):461-466. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112139-20231021-00184. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38548617 Review. Chinese.
-
A review of a priori regression models for warfarin maintenance dose prediction.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 12;9(12):e114896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114896. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25501765 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Validation and comparison between two warfarin dosing clinical algorithms and warfarin fixed dosing in specialized heart center: cross-sectional study.Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022 Jul-Sep;20(3):2722. doi: 10.18549/PharmPract.2022.3.2722. Epub 2022 Sep 14. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2022. PMID: 36733524 Free PMC article.
-
Developing Chinese race-specific warfarin dose prediction algorithms.Int J Clin Pharm. 2023 Jun;45(3):731-738. doi: 10.1007/s11096-023-01565-1. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Int J Clin Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36991222
-
Association between gene polymorphisms and initial warfarin therapy in patients after heart valve surgery.Pharmacol Rep. 2024 Apr;76(2):390-399. doi: 10.1007/s43440-024-00575-8. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Pharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38457019
-
Model-Informed Precision Dosing of Antibiotics in Pediatric Patients: A Narrative Review.Front Pediatr. 2021 Feb 23;9:624639. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.624639. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33708753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of warfarin population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics model in Han population based on Bayesian method.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 27;14(1):14846. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65048-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38937509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuan HY, Chen JJ, Lee MT, Wung JC, Chen YF, Charng MJ, et al. A novel functional VKORC1 promoter polymorphism is associated with inter-individual and inter-ethnic differences in warfarin sensitivity. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: 1745–51. - PubMed
-
- Singh O, Sandanaraj E, Subramanian K, Lee LH, Chowbay B. Influence of CYP4F2 rs2108622 (V433M) on warfarin dose requirement in Asian patients. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2011; 26: 130–6. - PubMed
-
- Ohno M, Yamamoto A, Ono A, Miura G, Funamoto M, Takemoto Y, et al. Influence of clinical and genetic factors on warfarin dose requirements among Japanese patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2009; 65: 1097–103. - PubMed
-
- Wen MS, Lee M, Chen JJ, Chuang HP, Lu LS, Chen CH, et al. Prospective study of warfarin in dose requirements based on CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2008; 84: 83–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

