RNA Silencing in Plants: Mechanisms, Technologies and Applications in Horticultural Crops
- PMID: 28217004
- PMCID: PMC5108043
- DOI: 10.2174/1389202917666160520103117
RNA Silencing in Plants: Mechanisms, Technologies and Applications in Horticultural Crops
Abstract
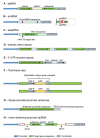
Understanding the fundamental nature of a molecular process or a biological pathway is often a catalyst for the development of new technologies in biology. Indeed, studies from late 1990s to early 2000s have uncovered multiple overlapping but functionally distinct RNA silencing pathways in plants, including the posttranscriptional microRNA and small interfering RNA pathways and the transcriptional RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway. These findings have in turn been exploited for developing artificial RNA silencing technologies such as hairpin RNA, artificial microRNA, intrinsic direct repeat, 3' UTR inverted repeat, artificial trans-acting siRNA, and virus-induced gene silencing technologies. Some of these RNA silencing technologies, such as the hairpin RNA technology, have already been widely used for genetic improvement of crop plants in agriculture. For horticultural plants, RNA silencing technologies have been used to increase disease and pest resistance, alter plant architecture and flowering time, improve commercial traits of fruits and flowers, enhance nutritional values, remove toxic compounds and allergens, and develop high-value industrial products. In this article we aim to provide an overview of the RNA silencing pathways in plants, summarize the existing RNA silencing technologies, and review the current progress in applying these technologies for the improvement of agricultural crops particularly horticultural crops.
Keywords: Double-stranded RNA; Hairpin RNA; Plants; RNA silencing; Virus; miRNA; siRNA.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
