Intra-Species and Inter-Kingdom Signaling of Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 28217110
- PMCID: PMC5289986
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00079
Intra-Species and Inter-Kingdom Signaling of Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
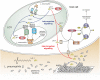
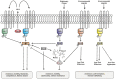
The ubiquitous Gram-negative bacterium Legionella pneumophila parasitizes environ mental amoebae and, upon inhalation, replicates in alveolar macrophages, thus causing a life-threatening pneumonia called "Legionnaires' disease." The opportunistic pathogen employs a bi-phasic life cycle, alternating between a replicative, non-virulent phase and a stationary, transmissive/virulent phase. L. pneumophila employs the Lqs (Legionella quorum sensing) system as a major regulator of the growth phase switch. The Lqs system comprises the autoinducer synthase LqsA, the homologous sensor kinases LqsS and LqsT, as well as a prototypic response regulator termed LqsR. These components produce, detect, and respond to the α-hydroxyketone signaling molecule LAI-1 (Legionella autoinducer-1, 3-hydroxypentadecane-4-one). LAI-1-mediated signal transduction through the sensor kinases converges on LqsR, which dimerizes upon phosphorylation. The Lqs system regulates the bacterial growth phase switch, pathogen-host cell interactions, motility, natural competence, filament production, and expression of a chromosomal "fitness island." Yet, LAI-1 not only mediates bacterial intra-species signaling, but also modulates the motility of eukaryotic cells through the small GTPase Cdc42 and thus promotes inter-kingdom signaling. Taken together, the low molecular weight compound LAI-1 produced by L. pneumophila and sensed by the bacteria as well as by eukaryotic cells plays a major role in pathogen-host cell interactions.
Keywords: Dictyostelium; Legionella; amoeba; autoinducer; bacterial pathogenesis; cell–cell communication; macrophage; phospho-transfer; quorum sensing; response regulator; sensor kinase; small molecule signaling; α-hydroxyketone.
Figures
References
-
- Borges V., Nunes A., Sampaio D. A., Vieira L., Machado J., Simoes M. J., et al. (2016).Legionella pneumophila strain associated with the first evidence of person-to-person transmission of Legionnaires’ disease: a unique mosaic genetic backbone. Sci. Rep. 6:26261 10.1038/srep26261 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

