Regulation of hepatic microRNA expression by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha
- PMID: 28217257
- PMCID: PMC5295159
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i4.191
Regulation of hepatic microRNA expression by hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha
Abstract
Aim: To uncover the role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) in regulating hepatic expression of microRNAs.
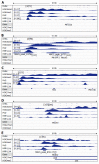
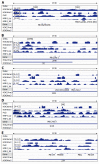
Methods: Microarray and real-time PCR were used to determine hepatic expression of microRNAs in young-adult mice lacking Hnf4α expression in liver (Hnf4α-LivKO). Integrative genomics viewer software was used to analyze the public chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing datasets for DNA-binding of HNF4α, RNA polymerase-II, and histone modifications to loci of microRNAs in mouse liver and human hepatoma cells. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to determine effects of HNF4α on the promoters of mouse and human microRNAs as well as effects of microRNAs on the untranslated regions (3'UTR) of two genes in human hepatoma cells.
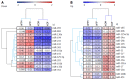
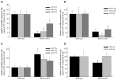
Results: Microarray data indicated that most microRNAs remained unaltered by Hnf4α deficiency in Hnf4α-LivKO mice. However, certain liver-predominant microRNAs were down-regulated similarly in young-adult male and female Hnf4α-LivKO mice. The down-regulation of miR-101, miR-192, miR-193a, miR-194, miR-215, miR-802, and miR-122 as well as induction of miR-34 and miR-29 in male Hnf4α-LivKO mice were confirmed by real-time PCR. Analysis of public chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing data indicates that HNF4α directly binds to the promoters of miR-101, miR-122, miR-194-2/miR-192 and miR-193, which is associated with histone marks of active transcription. Luciferase reporter assay showed that HNF4α markedly activated the promoters of mouse and human miR-101b/miR-101-2 and the miR-194/miR-192 cluster. Additionally, miR-192 and miR-194 significantly decreased activities of luciferase reporters for the 3'UTR of histone H3F3 and chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 1 (CHD1), respectively, suggesting that miR-192 and miR-194 might be important in chromosome remodeling through directly targeting H3F3 and CHD1.
Conclusion: HNF4α is essential for hepatic basal expression of a group of liver-enriched microRNAs, including miR-101, miR-192, miR-193a, miR-194 and miR-802, through which HNF4α may play a major role in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and maintenance of the epigenome in liver.
Keywords: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; Human; Knockout; Liver; Mice; miR-101; miR-122; miR-192; miR-194; miR-802.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

