Structural characterization of two tetra-chlorido-zincate salts of 4-carb-oxy-1 H-imidazol-3-ium: a salt hydrate and a co-crystal salt hydrate
- PMID: 28217334
- PMCID: PMC5290557
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017000317
Structural characterization of two tetra-chlorido-zincate salts of 4-carb-oxy-1 H-imidazol-3-ium: a salt hydrate and a co-crystal salt hydrate
Abstract
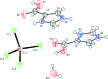
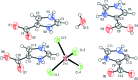
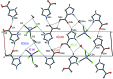
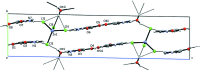
Imidazole-containing compounds exhibit a myriad of pharmacological activities. Two tetra-chlorido-zincate salts of 4-carb-oxy-1H-imidazol-3-ium, ImHCO2H+, are reported. Bis(4-carb-oxy-1H-imidazol-3-ium) tetra-chlorido-zincate monohydrate, (C4H5N2O2)2[ZnCl4]·H2O, (I), crystallizes as a monohydrate salt, while bis-(4-carb-oxy-1H-imidazol-3-ium) tetra-chlorido-zincate bis-(1H-imidazol-3-ium-4-carboxyl-ato) monohydrate, (C4H5N2O2)2[ZnCl4]·2C4H4N2O2·H2O, (II), is a co-crystal salt with six residues: two ImHCO2H+ cations, two formula units of the zwitterionic 1H-imidazol-3-ium-4-carboxyl-ate, ImHCO2, one tetra-chlorido-zincate anion and one water mol-ecule disordered over two sites in a 0.60 (4):0.40 (4) ratio. The geometric parameters of the ImHCO2H+ and the ImHCO2 moieties are the same within the standard uncertainties of the measurements. Both compounds exhibit extensive hydrogen bonding, including involvement of the tetra-chlorido-zincate anion, resulting in inter-connected chains of anions joined by water mol-ecules.
Keywords: co-crystal; crystal structure; hydrate; imidazolium; tetrachloridozincate.
Figures



References
-
- Boskovic, C., Folting, K. & Christou, G. (2000). Polyhedron, 19, 2111–2118.
-
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bulic, B., Pickhardt, M. & Mandelkow, E. (2013). J. Med. Chem. 56, 4135–4155. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
