Utility of immunofluorescence in dermatology
- PMID: 28217464
- PMCID: PMC5297263
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-5178.198774
Utility of immunofluorescence in dermatology
Abstract
Immunofluorescence (IF) tests have redefined our understanding of many immune-mediated skin diseases, especially autoimmune blistering diseases (AIBDs). Nomenclature of certain AIBDs (for example, linear IgA diseases and IgA pemphigus) has been done based solely on the finding of tissue-bound immunoreactants as detected by IF tests. Direct and indirect are the two major types of IF tests; they are not only useful in the diagnosis but also guide the clinician in the treatment at least in certain AIBDs, as the titer of circulating antibodies as detected by IF reflects the disease activity. In this review, we describe techniques, various types of IF, and its modification.
Keywords: Autoimmune blistering diseases; diagnosis; immunofluorescence tests.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



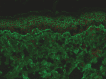

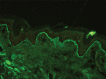
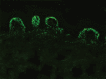
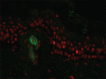

References
-
- Vassileva S. Immunofluorescence in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 1993;32:153–61. - PubMed
-
- Chhabra S, Minz RW, Saikia B. Immunofluorescence in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:677–91. - PubMed
-
- Mohan KH, Pai S, Rao R, Sripathi H, Prabhu S. Techniques of immunofluorescence and their significance. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:415–9. - PubMed
-
- Sawant P, Kshar A, Byakodi R, Paranjpe A. Immunofluorescence in oral mucosal diseases – A review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Radiol. 2014;2:6–10.
-
- Aoki V, Sousa JX, Jr, Fukumori LM, Périgo AM, Freitas EL, Oliveira ZN. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence. An Bras Dermatol. 2010;85:490–500. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

