Secukinumab efficacy and safety in indian patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: Sub-analysis from FIXTURE, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study
- PMID: 28217466
- PMCID: PMC5297264
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-5178.198765
Secukinumab efficacy and safety in indian patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: Sub-analysis from FIXTURE, a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study
Abstract
Title: Secukinumab efficacy and safety in Indian patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: sub-analysis from FIXTURE (Full Year Investigative Examination of Secukinumab vs. Etanercept Using Two Dosing Regimens to Determine Efficacy in Psoriasis), a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study.
Background: Evidence has suggested Interleukin (IL)-17A to be an important effector cytokine in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Here, we report results for an Indian sub-population from a multinational study FIXTURE, designed to assess the safety, tolerability, and long-term efficacy of fully human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
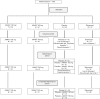
Materials and methods: In this double-dummy, placebo controlled, 52-weeks phase 3 study FIXTURE, 149 Indian patients were randomized 1:1:1:1 to receive secukinumab at a dose of 300 mg or 150 mg, etanercept, or placebo. The study objective was to show the superiority of secukinumab over placebo at week 12, vis-à-vis proportion of patients achieving a reduction of 75% or more from the baseline in the psoriasis area-and-severity index score (PASI 75) and a score of 0 (clear) or 1 (almost clear) on a 5-point modified investigator's global assessment (IGA mod 2011) (co-primary end points).
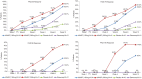
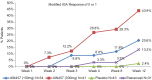
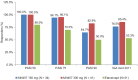
Results: At week 12, 61.0% and 55.9% patients in secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg groups, respectively, achieved PASI 75 response compared to 20.0% in the etanercept and 7.1% in the placebo groups. Similarly, IGA mod 2011 0 or 1 response was achieved by 43.9% and 20.6% in patients in the secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg group, respectively, vs. 13.3% in the etanercept and 2.4% in the placebo groups at week 12. Likewise, higher proportions of patients in secukinumab 300 mg (41.5%) and 150 mg (20.6%) group were PASI 90 responders at week 12 than those in the etanercept (10.0%) or placebo (0.0%) groups. The incidences of adverse events (AEs), during the induction period were similar in all the treatment groups. Overall secukinumab was well-tolerated at both doses in the Indian sub-population.
Conclusion: The results from the Indian sub-population suggest that secukinumab is an efficacious and safe drug for use in moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis.
Keywords: Interleukin (IL)-17A; PASI 75; plaque psoriasis; secukinumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Ramesh Bhat has received research grants from Novartis Pharmaceuticals. Amit Thavkar is an employee of Novartis India Limited.
Figures
References
-
- Flatz L, Conrad C. Role of T-cell-mediated inflammation in psoriasis: Pathogenesis and targeted therapy. Psoriasis Targets Ther. 2013;3:1–10.
-
- Dogra S, Yadav S. Psoriasis in India: Prevalence and pattern. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Girolomoni G, Mrowietz U, Paul C. Psoriasis: Rationale for targeting interleukin-17. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:717–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

