Association of anxiety, depression, and psychological distress in people with and without functional dyspepsia
- PMID: 28217633
- PMCID: PMC5220680
- DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.190936
Association of anxiety, depression, and psychological distress in people with and without functional dyspepsia
Abstract
Background: Current studies have indicated a high ratio of psychological problems in functional dyspepsia (FD) which causes disturbance in its management, so recognition these problems help the process of treatment.
Materials and methods: This was a cross-sectional study with a sample size of 4763 carried out in Isfahan University of Medical Sciences in 2011. Modified ROME III questionnaire was used to evaluate FD symptoms. Hospital anxiety and depression scale and 12-item General Health Questionnaire-12 was used to assess the psychological issue. Logistic regression analysis was used to assess the association of psychological problems and FD.
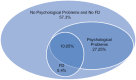
Results: We showed that overly 654 (13.7%), 1338 (28.1%), and 1067 (22.4%) of participants, respectively had anxiety, depression, and of psychological distress. Seven hundred and ten (15.5%) participants were diagnosed with FD. Of all participants Mean scores of anxiety (P < 0.001), depression (P < 0.001), and psychological distress (P < 0.001) in participants with FD were significantly more than those with no FD. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that psychological problems, whether in the form of psychological distress odds ratio (OR): 2 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.3-3) and OR: 1.3 (95% CI: 1.1-1.7) in males and females, respectively, anxiety OR: 2.4 (95% CI: 1.5-3.9) and OR: 2.3 (95% CI: 1.7-3.2) in males and females, respectively) or depression OR: 2.2 (95% CI: 1.5-3.3) and OR: 1.7 (95% CI: 1.3-2.3) in males and females, respectively) were significantly linked to FD in both genders.
Conclusions: The prevalence of FD is less in males than females, but psychological links were stronger in males. Thus, it is essential to consider and detect the psychological distress in these patients.
Keywords: Anxiety; depression psychological distress; functional dyspepsia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Drossman DA, Corazziari E, Delvaux M, Spiller RC, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, editors. The Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. 3rd ed. McLean, Va: Degnon Associates; 2006. p. 943.
-
- Chang L. Review article: Epidemiology and quality of life in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004;20(Suppl 7):31–9. - PubMed
-
- Drossman DA, Dumitrascu DL. Rome III: New standard for functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006;15:237–41. - PubMed
-
- Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1377–90. - PubMed
-
- Vege SS, Locke GR, 3rd, Weaver AL, Farmer SA, Melton LJ, 3rd, Talley NJ. Functional gastrointestinal disorders among people with sleep disturbances: A population-based study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004;79:1501–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources