Plin5 alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress through inhibiting the lipolysis of lipid droplets
- PMID: 28218306
- PMCID: PMC5316932
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42574
Plin5 alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress through inhibiting the lipolysis of lipid droplets
Abstract
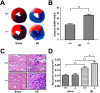
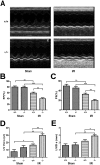
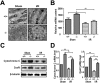
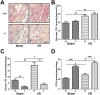
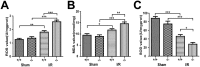
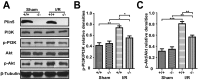
Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury is a complex pathophysiological process. Current research has suggested that energy metabolism disorders, of which the abnormal consumption of fatty acids is closely related, compose the main pathological basis for myocardial I/R injury. Lipid droplets (LD) are critical regulators of lipid metabolism by LD-associated proteins. Among the lipid droplet proteins, the perilipin family members regulate lipolysis and lipogenesis through different mechanisms. Plin5, an important perilipin protein, promotes LD generation and lowers fatty acid oxidation, thus protecting the myocardium from lipotoxicity. This study investigated the protective effects of Plin5 in I/R myocardium. Our results indicated that Plin5 deficiency exacerbated the myocardial infarct area, aggravated left ventricular systolic dysfunction, reduced lipid storage, and elevated free fatty acids. Plin5-deficient myocardium exhibited severely damaged mitochondria, elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, and decreased superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Furthermore, the decreased phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt in Plin5-null cardiomyocytes might contribute to I/R injury aggravation. In conclusion, Plin5, a new regulator of myocardial lipid metabolism, decreases free fatty acid peroxidation by inhibiting the lipolysis of intracellular lipid droplets, thus providing cardioprotection against I/R injury and shedding new light on therapeutic solutions for I/R diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolated Plin5-deficient cardiomyocytes store less lipid droplets than normal, but without increased sensitivity to hypoxia.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021 Apr;1866(4):158873. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158873. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021. PMID: 33373698
-
Plin5 deficiency exacerbates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure by enhancing myocardial fatty acid oxidation and oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Sep;141:372-382. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.07.006. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31291602
-
Perilipin 5 fine-tunes lipid oxidation to metabolic demand and protects against lipotoxicity in skeletal muscle.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 6;6:38310. doi: 10.1038/srep38310. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27922115 Free PMC article.
-
Perilipin 5, a lipid droplet protein adapted to mitochondrial energy utilization.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Apr;25(2):110-7. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000057. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 24535284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plin5 Bidirectionally Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Oxidative Tissues.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 31;2022:4594956. doi: 10.1155/2022/4594956. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35401929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plin5, a New Target in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 25;2022:2122856. doi: 10.1155/2022/2122856. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35509833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plin5 inhibits proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cell through interacting with PGC-1α following vascular injury.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):10665-10678. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2065762. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35470759 Free PMC article.
-
Role of autophagy in a model of obesity: A long‑term high fat diet induces cardiac dysfunction.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Sep;18(3):3251-3261. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9301. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30066870 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Effects of Chinese herbal medicine and the underlying mechanisms.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Feb;15(2):101051. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101051. Epub 2024 Jul 23. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 39931135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of lipid droplets and related proteins in metabolic diseases.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Jul 19;23(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02212-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39030618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jennings R. B., Sommers H. M., Smyth G. A., Flack H. A. & Linn H. Myocardial necrosis induced by temporary occlusion of a coronary artery in the dog. Archives of pathology 70, 68–78 (1960). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

