Mapping DNA methylation with high-throughput nanopore sequencing
- PMID: 28218897
- PMCID: PMC5704956
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4189
Mapping DNA methylation with high-throughput nanopore sequencing
Abstract
DNA chemical modifications regulate genomic function. We present a framework for mapping cytosine and adenosine methylation with the Oxford Nanopore Technologies MinION using this nanopore sequencer's ionic current signal. We map three cytosine variants and two adenine variants. The results show that our model is sensitive enough to detect changes in genomic DNA methylation levels as a function of growth phase in Escherichia coli.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing financial interests
M.A. is a consultant to Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
Figures

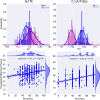
Comment in
-
Epigenetics: Rich pore methods for DNA methylation detection.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 Mar 15;18(4):209. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.18. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28293030 No abstract available.
-
Nanopore sequencing meets epigenetics.Nat Methods. 2017 Mar 31;14(4):347-348. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4240. Nat Methods. 2017. PMID: 28362434 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schübeler D. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature. 2015;517:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Smith ZD, Meissner A. DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013;14:204–220. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-Romero MA, Cota I, Casadesús J. DNA methylation in bacteria: from the methyl group to the methylome. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015;25:9–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

