The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors
- PMID: 28218907
- PMCID: PMC5332298
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3473
The LINK-A lncRNA interacts with PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 to hyperactivate AKT and confer resistance to AKT inhibitors
Abstract
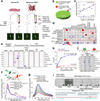
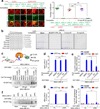
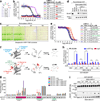
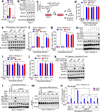
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 or PIP3) mediates signalling pathways as a second messenger in response to extracellular signals. Although primordial functions of phospholipids and RNAs have been hypothesized in the 'RNA world', physiological RNA-phospholipid interactions and their involvement in essential cellular processes have remained a mystery. We explicate the contribution of lipid-binding long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in cancer cells. Among them, long intergenic non-coding RNA for kinase activation (LINK-A) directly interacts with the AKT pleckstrin homology domain and PIP3 at the single-nucleotide level, facilitating AKT-PIP3 interaction and consequent enzymatic activation. LINK-A-dependent AKT hyperactivation leads to tumorigenesis and resistance to AKT inhibitors. Genomic deletions of the LINK-A PIP3-binding motif dramatically sensitized breast cancer cells to AKT inhibitors. Furthermore, meta-analysis showed the correlation between LINK-A expression and incidence of a single nucleotide polymorphism (rs12095274: A > G), AKT phosphorylation status, and poor outcomes for breast and lung cancer patients. PIP3-binding lncRNA modulates AKT activation with broad clinical implications.
Figures



Comment in
-
Non-coding RNA: The cancer link(RNA) between PIP3 and AKT.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;18(4):212-213. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.18. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28248320 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wymann MP, Schneiter R. Lipid signalling in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:162–176. - PubMed
-
- Mayer IA, Arteaga CL. The PI3K/AKT Pathway as a Target for Cancer Treatment. Annual review of medicine. 2016;67:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Gaullier JM, et al. FYVE fingers bind PtdIns(3)P. Nature. 1998;394:432–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

