Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of ligamentous injuries on conventional MRI after simple elbow dislocation
- PMID: 28219360
- PMCID: PMC5319117
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1451-2
Interobserver and intraobserver agreement of ligamentous injuries on conventional MRI after simple elbow dislocation
Abstract
Background: The primary objective of this study was to assess the interobserver and intraobserver agreement on ligamentous injuries on conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in acute simple elbow dislocation. The secondary objectives were to determine the interobserver agreement on the assessment of joint congruity, joint effusion, loose bodies and chondral lesions on conventional MRI.
Methods: Conventional MRIs (1.5 Tesla, elbow specific surface coil) of 30 patients (40.7 years; range 14-72) with simple elbow dislocations were evaluated by four blinded examiners. An analysis of the interobserver agreement of all raters and for several subgroups (radiologists, orthopaedics, experienced, non-experienced) was performed. The examiners assessed the integrity (intact, partial tear, complete tear) of the lateral collateral ligament (LCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), extensor and flexor tendons, as well as the presence of joint congruity, joint effusion, loose bodies and chondral lesions. Agreement strength, correlation and proportion of exact agreement were determined for interobserver agreement, and intraobserver agreement analyses.
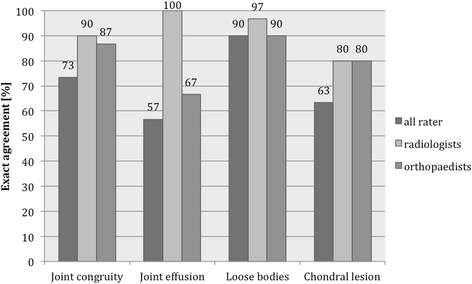
Results: Interobserver agreement of all examiners was fair to moderate for collateral ligaments (LCL: 0.441, MCL: 0.275). Exact agreement of all raters was found in 33.3% for the LCL and in 26.7% for the MCL. The both experienced examiners showed highest agreement strength for the LCL (0.619) and the radiologists showed highest agreement strength for the MCL (0.627), the proportion of exact agreement was 60.0% in both categories. A high proportion of exact agreement regarding joint congruity (90%), joint effusion (100%), loose bodies (96.7%) and chondral lesion (80%) was found among the radiologists. The evaluation of the intraobserver agreement revealed slight to substantial agreement (0.227 to 0.718) for the collateral ligaments.
Conclusions: This study shows difficulties in the evaluation of ligaments by conventional MRI technique as demonstrated by a weak inter- and intraobserver agreement. This should be the basis to develop new MRI quality standards with special focus on coronal oblique reconstructions to improve the evaluation of ligament injuries after simple elbow dislocations.
Keywords: Coronal oblique view; Elbow dislocation; Interobserver; Intraobserver; Lateral collateral ligaments; Lateral ulnar collateral ligament; MRI; Medial collateral ligaments; Simple elbow dislocation.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

