Impact of Coronary Artery Disease Severity Assessed With the SYNTAX Score on Outcomes Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
- PMID: 28219920
- PMCID: PMC5523783
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005070
Impact of Coronary Artery Disease Severity Assessed With the SYNTAX Score on Outcomes Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
Background: The influence of coronary artery disease (CAD) on clinical and echocardiographic outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is still controversial. We sought to evaluate the impact of CAD severity as measured by the SYNTAX score (SS) on patients undergoing TAVR.
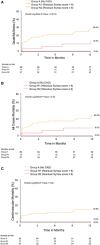
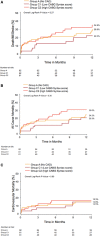
Methods and results: A total of 377 patients who underwent TAVR in 2 high-volume centers in North America were included in our retrospective analysis. A blinded angiographic core laboratory calculated the SS on all available coronary angiograms with the use of quantitative coronary analysis. Patients were stratified into 4 groups: (1) no CAD (SS=0); (2) low SS (SS between 1 and 22); (3) intermediate SS (SS between 23 and 32); and (4) high SS (SS ≥33). Patients who had undergone percutaneous coronary intervention within 6 months prior to TAVR were separated into 2 categories based on their residual SS (<8 and ≥8). Patients with previous coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) were divided into 2 groups: (1) low CABG SS and (2) high CABG SS. The primary end point was a composite of all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke. At 30 days and 1 year, both the presence and the severity of CAD had no impact on the rate of the combined primary end point and on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and myocardial infarction. Patients with less complete revascularization (residual SS ≥8 versus residual SS <8 and low CABG SS versus high CABG SS, had similar rates of the combined primary end point, all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, MI, and stroke, at both 30 days and 1 year.
Conclusions: In our core laboratory-validated study, neither the severity of CAD nor completeness of revascularization after percutaneous coronary intervention or CABG were associated with clinical outcomes after TAVR, at both 30 days and 1 year.
Keywords: SYNTAX score; aortic stenosis; coronary artery disease; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical Conundrum of Coronary Artery Disease and Aortic Valve Stenosis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Feb 20;6(2):e005593. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.005593. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28219922 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rapp AH, Hillis LD, Lange RA, Cigarroa JE. Prevalence of coronary artery disease in patients with aortic stenosis with and without angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 2001;87:1216–1217; A7. - PubMed
-
- Vandeplas A, Willems JL, Piessens J, De Geest H. Frequency of angina pectoris and coronary artery disease in severe isolated valvular aortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 1988;62:117–120. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura RA, Otto CM, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP, Guyton RA, O'Gara PT, Ruiz CE, Skubas NJ, Sorajja P, Sundt TM, Thomas JD; American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:e57–e185. - PubMed
-
- Stewart BF, Siscovick D, Lind BK, Gardin JM, Gottdiener JS, Smith VE, Kitzman DW, Otto CM. Clinical factors associated with calcific aortic valve disease. Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997;29:630–634. - PubMed
-
- Pibarot P, Dumesnil JG. Improving assessment of aortic stenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:169–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

