Systems Biology-Derived Discoveries of Intrinsic Clocks
- PMID: 28220104
- PMCID: PMC5292584
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00025
Systems Biology-Derived Discoveries of Intrinsic Clocks
Abstract
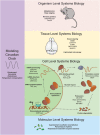
A systems approach to studying biology uses a variety of mathematical, computational, and engineering tools to holistically understand and model properties of cells, tissues, and organisms. Building from early biochemical, genetic, and physiological studies, systems biology became established through the development of genome-wide methods, high-throughput procedures, modern computational processing power, and bioinformatics. Here, we highlight a variety of systems approaches to the study of biological rhythms that occur with a 24-h period-circadian rhythms. We review how systems methods have helped to elucidate complex behaviors of the circadian clock including temperature compensation, rhythmicity, and robustness. Finally, we explain the contribution of systems biology to the transcription-translation feedback loop and posttranslational oscillator models of circadian rhythms and describe new technologies and "-omics" approaches to understand circadian timekeeping and neurophysiology.
Keywords: RNA sequencing; circadian rhythm; models; neurophysiology; ribosome profiling; systems biology; theory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
It is not the parts, but how they interact that determines the behaviour of circadian rhythms across scales and organisms.Interface Focus. 2014 Jun 6;4(3):20130076. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2013.0076. Interface Focus. 2014. PMID: 24904739 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature robustness in Arabidopsis circadian clock models is facilitated by repressive interactions, autoregulation, and three-node feedbacks.J Theor Biol. 2021 Jan 21;509:110495. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2020.110495. Epub 2020 Sep 20. J Theor Biol. 2021. PMID: 32966827
-
Chronobiology at the cellular and molecular levels: models and mechanisms for circadian timekeeping.Am J Anat. 1983 Dec;168(4):389-431. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001680404. Am J Anat. 1983. PMID: 6229999 Review.
-
Genetics and molecular biology of rhythms in Drosophila and other insects.Adv Genet. 2003;48:1-280. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(03)48000-0. Adv Genet. 2003. PMID: 12593455 Review.
-
Sensory conflict disrupts circadian rhythms in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis.Elife. 2023 Apr 6;12:e81084. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81084. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37022138 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Holistic Needs Assessment of Cancer Survivors-Supporting the Process Through Digital Monitoring of Circadian Physiology.Integr Cancer Ther. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15347354221123525. doi: 10.1177/15347354221123525. Integr Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 36154506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic proteomic profiling identifies a landscape of targets for circadian clock-modulating compounds.Life Sci Alliance. 2019 Dec 2;2(6):e201900603. doi: 10.26508/lsa.201900603. Print 2019 Dec. Life Sci Alliance. 2019. PMID: 31792063 Free PMC article.
-
What's next for chronobiology and drug discovery.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017 Dec;12(12):1181-1185. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2017.1378179. Epub 2017 Sep 11. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28893103 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PRD-2 directly regulates casein kinase I and counteracts nonsense-mediated decay in the Neurospora circadian clock.Elife. 2020 Dec 9;9:e64007. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64007. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33295874 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Therapeutic Potential of Small-Molecule Modulators of Circadian Systems.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Jan 6;58:231-252. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-052645. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 28968186 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

