Synchronization by Daytime Restricted Food Access Modulates the Presence and Subcellular Distribution of β-Catenin and Its Phosphorylated Forms in the Rat Liver
- PMID: 28220106
- PMCID: PMC5292920
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00014
Synchronization by Daytime Restricted Food Access Modulates the Presence and Subcellular Distribution of β-Catenin and Its Phosphorylated Forms in the Rat Liver
Abstract
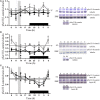
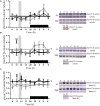
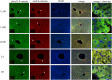
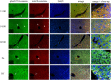
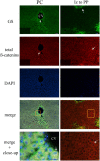
β-catenin, the principal effector of the Wnt pathway, is also one of the cadherin cell adhesion molecules; therefore, it fulfills signaling and structural roles in most of the tissues and organs. It has been reported that β-catenin in the liver regulates metabolic responses such as gluconeogenesis and histological changes in response to obesity-promoting diets. The function and cellular location of β-catenin is finely modulated by coordinated sequences of phosphorylation-dephosphorylation events. In this article, we evaluated the levels and cellular localization of liver β-catenin variants, more specifically β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 33 (this phosphorylation provides recognizing sites for β-TrCP, which results in ubiquitination and posterior proteasomal degradation of β-catenin) and β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 675 (phosphorylation that enhances signaling and transcriptional activity of β-catenin through recruitment of different transcriptional coactivators). β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 33 in the nucleus shows day-night fluctuations in their expression level in the Ad Libitum group. In addition, we used a daytime restricted feeding (DRF) protocol to show that the above effects are sensitive to food access-dependent circadian synchronization. We found through western blot and immunohistochemical analyses that DRF protocol promoted (1) higher total β-catenins levels mainly associated with the plasma membrane, (2) reduced the presence of cytoplasmic β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 33, (3) an increase in nuclear β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 675, (4) differential co-localization of total β-catenins/β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 33 and total β-catenins/β-catenin phosphorylated in serine 675 at different temporal points along day and in fasting and refeeding conditions, and (5) differential liver zonation of β-catenin variants studied along hepatic acinus. In conclusion, the present data comprehensively characterize the effect food synchronization has on the presence, subcellular distribution, and liver zonation of β-catenin variants. These results are relevant to understand the set of metabolic and structural liver adaptations that are associated with the expression of the food entrained oscillator (FEO).
Keywords: food entrained oscillator; liver; microscopy; phosphorylation; β-catenin variants.
Figures





References
-
- Challet E, Solberg LC, Turek FW. Entrainment in calorie-restricted mice: conflicting zeitgebers and free-running conditions. Am J Physiol (1998) 274(6 Pt 2):R1751–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

