Simultaneous detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Middle East respiratory syndrome, and related bat coronaviruses by real-time reverse transcription PCR
- PMID: 28220326
- PMCID: PMC7086956
- DOI: 10.1007/s00705-017-3281-9
Simultaneous detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Middle East respiratory syndrome, and related bat coronaviruses by real-time reverse transcription PCR
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Simultaneous detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Middle East respiratory syndrome, and related bat coronaviruses by real-time reverse transcription PCR.Arch Virol. 2018 Mar;163(3):819. doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3677-6. Arch Virol. 2018. PMID: 29273879 Free PMC article.
Abstract
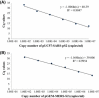
Since severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronaviruses (CoVs) share similar characteristics with respect to clinical signs, etiology, and transmission, methods for a rapid and accurate differential diagnosis are important. Therefore, the aim of this study was to develop a duplex real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR method for the simultaneous detection of these viruses. Primers and probes that target the conserved spike S2 region of human SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and their related bat CoVs were designed. The results of real-time RT-PCR showed specific reactions for each virus with adequate detection limits of 50-100 copies/mL and 5-100 copies/mL using pUC57-SARS-pS2 (a template for SARS-CoV) and pGEM-MERS-S2 (a template for MERS-CoV), respectively. In addition, this real-time RT-PCR system was able to detect the target viruses SARS-like bat CoV and MERS-CoV in bat fecal samples and sputum of MERS patients, respectively. Therefore, this newly developed real-time RT-PCR method is expected to detect not only SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV in humans but also several bat CoVs that are closely related to these viruses in bats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Ge X-Y, Li J-L, Yang X-L, Chmura AA, Zhu G, Epstein JH, Mazet JK, Hu B, Zhang W, Peng C, Zhang YJ, Luo CM, Tan B, Wang N, Zhu Y, Crameri G, Zhang SY, Wang LF, Daszak P, Shi ZL. Isolation and characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2013;503:535–538. doi: 10.1038/nature12711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

