Epigenetic determinants of space radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction
- PMID: 28220892
- PMCID: PMC5318883
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42885
Epigenetic determinants of space radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction
Abstract
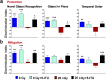
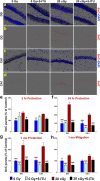
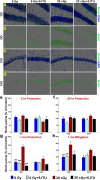
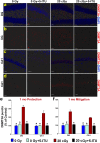
Among the dangers to astronauts engaging in deep space missions such as a Mars expedition is exposure to radiations that put them at risk for severe cognitive dysfunction. These radiation-induced cognitive impairments are accompanied by functional and structural changes including oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and degradation of neuronal architecture. The molecular mechanisms that dictate CNS function are multifaceted and it is unclear how irradiation induces persistent alterations in the brain. Among those determinants of cognitive function are neuroepigenetic mechanisms that translate radiation responses into altered gene expression and cellular phenotype. In this study, we have demonstrated a correlation between epigenetic aberrations and adverse effects of space relevant irradiation on cognition. In cognitively impaired irradiated mice we observed increased 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine levels in the hippocampus that coincided with increased levels of the DNA methylating enzymes DNMT3a, TET1 and TET3. By inhibiting methylation using 5-iodotubercidin, we demonstrated amelioration of the epigenetic effects of irradiation. In addition to protecting against those molecular effects of irradiation, 5-iodotubercidin restored behavioral performance to that of unirradiated animals. The findings of this study establish the possibility that neuroepigenetic mechanisms significantly contribute to the functional and structural changes that affect the irradiated brain and cognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


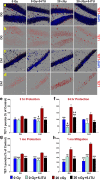
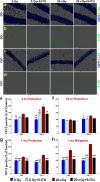
References
-
- Raber J., Marzulla T., Stewart B., Kronenberg A. & Turker M. Silicon Irradiation Impairs Contextual Fear Memory in B6D2F1 Mice. Radiat Res (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

