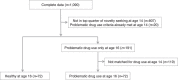
Blunted ventral striatal responses to anticipated rewards foreshadow problematic drug use in novelty-seeking adolescents
- PMID: 28221370
- PMCID: PMC5321762
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14140
Blunted ventral striatal responses to anticipated rewards foreshadow problematic drug use in novelty-seeking adolescents
Abstract
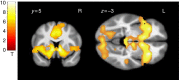
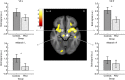
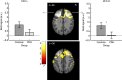
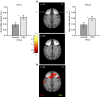
Novelty-seeking tendencies in adolescents may promote innovation as well as problematic impulsive behaviour, including drug abuse. Previous research has not clarified whether neural hyper- or hypo-responsiveness to anticipated rewards promotes vulnerability in these individuals. Here we use a longitudinal design to track 144 novelty-seeking adolescents at age 14 and 16 to determine whether neural activity in response to anticipated rewards predicts problematic drug use. We find that diminished BOLD activity in mesolimbic (ventral striatal and midbrain) and prefrontal cortical (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex) regions during reward anticipation at age 14 predicts problematic drug use at age 16. Lower psychometric conscientiousness and steeper discounting of future rewards at age 14 also predicts problematic drug use at age 16, but the neural responses independently predict more variance than psychometric measures. Together, these findings suggest that diminished neural responses to anticipated rewards in novelty-seeking adolescents may increase vulnerability to future problematic drug use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jupp B. & Dalley J. W. Behavioral endophenotypes of drug addiction: Etiological insights from neuroimaging studies. Neuropharmacology 76, (Pt B): 487–497 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Steinberg L. et al.. Age differences in sensation seeking and impulsivity as indexed by behavior and self-report: evidence for a dual systems model. Dev. Psychol. 44, 1764–1778 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Le Bon O. et al.. Personality profile and drug of choice; a multivariate analysis using Cloninger's TCI on heroin addicts, alcoholics, and a random population group. Drug Alcohol Depend. 73, 175–182 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

