Remediating 1,4-dioxane-contaminated water with slow-release persulfate and zerovalent iron
- PMID: 28222371
- PMCID: PMC5409506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.044
Remediating 1,4-dioxane-contaminated water with slow-release persulfate and zerovalent iron
Abstract
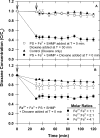
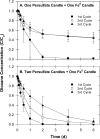
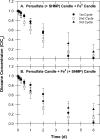
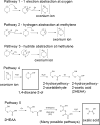
1,4-dioxane is an emerging contaminant that was used as a corrosion inhibitor with chlorinated solvents. Metal-activated persulfate can degrade dioxane but reaction kinetics have typically been characterized by a rapid decrease during the first 30 min followed by either a slower decrease or no further change (i.e., plateau). Our objective was to identify the factors responsible for this plateau and then determine if slow-release formulations of sodium persulfate and Fe0 could provide a more sustainable degradation treatment. We accomplished this by conducting batch experiments where Fe0-activated persulfate was used to treat dioxane. Treatment variables included the timing at which the dioxane was added to the Fe0-persulfate reaction (T = 0 and 30 min) and including various products of the Fe0-persulfate reaction at T = 0 min (Fe2+, Fe3+, and SO42-). Results showed that when dioxane was spiked into the reaction at 30 min, no degradation occurred; this is in stark contrast to the 60% decrease observed when added at T = 0 min. Adding Fe2+ at the onset (T = 0 min) also severely halted the reaction and caused a plateau. This indicates that excess ferrous iron produced from the Fe0-persulfate reaction scavenges sulfate radicals and prevents further dioxane degradation. By limiting the release of Fe0 in a slow-release wax formulation, degradation plateaus were avoided and 100% removal of dioxane observed. By using 14C-labeled dioxane, we show that ∼40% of the dioxane carbon is mineralized within 6 d. These data support the use of slow-release persulfate and zerovalent iron to treat dioxane-contaminated water.
Keywords: Chlorinated solvents; Dioxane; Persulfate; Slow-release oxidants; TCE.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Anipsitakis GP, Dionysiou DD. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ Sci Technol. 2004a;38:3705–3712. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett PD, Cotman JD. The kinetics of the decomposition of potassium persulfate in aqueous solutions of methanol. J Am Chem Soc. 1949;71:1419–1425.
-
- Bigda RJ. Consider Fenton’s chemistry for wastewater treatment. Chem Eng Progress. 1995 Dec;1995:62–66.
-
- Chokejaroenrat C, Kananizadeh N, Sakulthaew C, Comfort S, Li Y. Improving the sweeping efficiency of permanganate into low permeable zones to treat TCE: Experimental results and model development. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47:13031–13038. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

