Spatiotemporal dynamics of HIV-1 transmission in France (1999-2014) and impact of targeted prevention strategies
- PMID: 28222757
- PMCID: PMC5322782
- DOI: 10.1186/s12977-017-0339-4
Spatiotemporal dynamics of HIV-1 transmission in France (1999-2014) and impact of targeted prevention strategies
Abstract
Background: Characterizing HIV-1 transmission networks can be important in understanding the evolutionary patterns and geospatial spread of the epidemic. We reconstructed the broad molecular epidemiology of HIV from individuals with primary HIV-1 infection (PHI) enrolled in France in the ANRS PRIMO C06 cohort over 15 years.
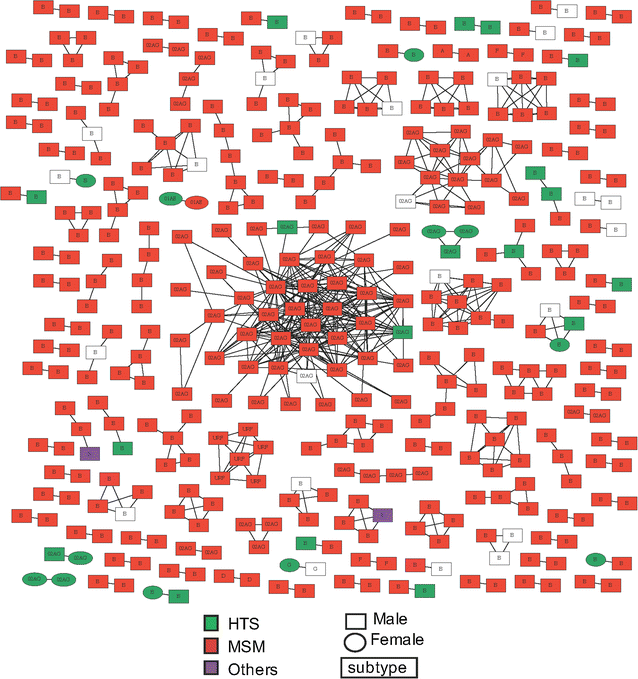
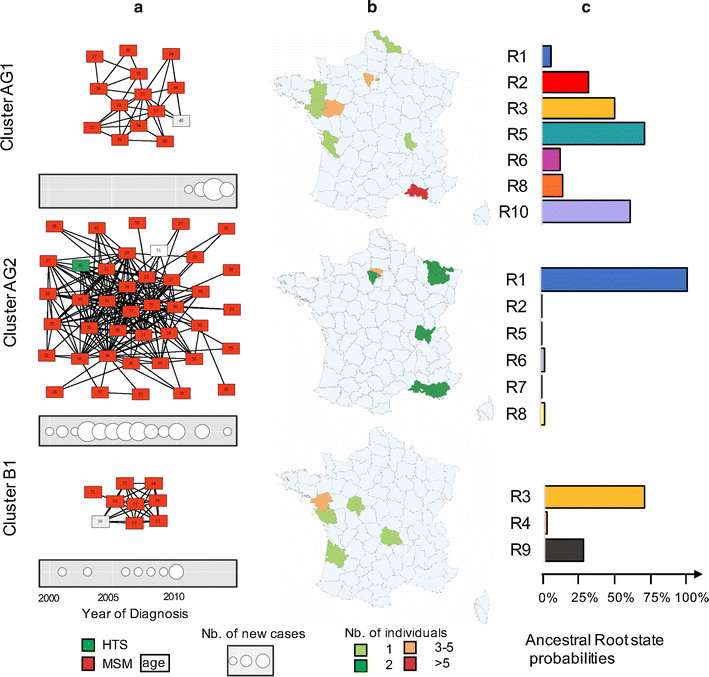
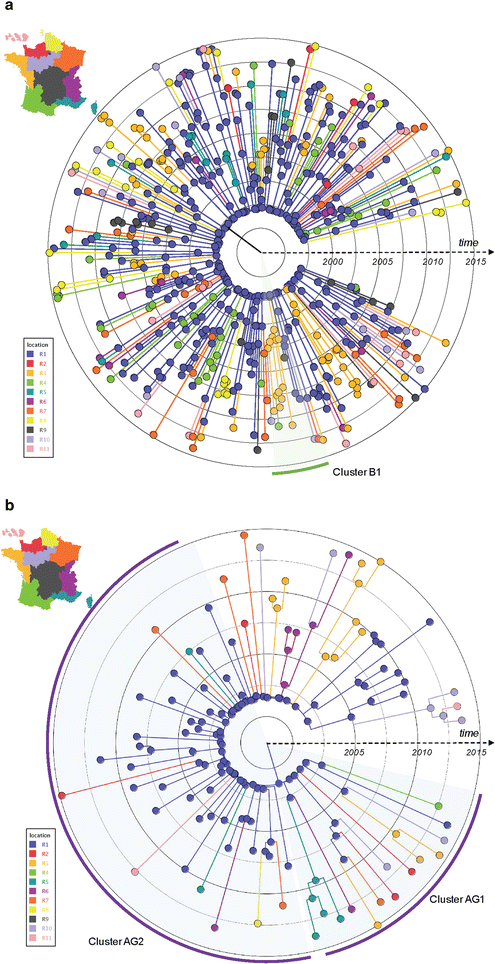
Results: Sociodemographic, geographic, clinical, biological and pol sequence data from 1356 patients were collected between 1999 and 2014. Network analysis was performed to infer genetic relationships, i.e. clusters of transmission, between HIV-1 sequences. Bayesian coalescent-based methods were used to examine the temporal and spatial dynamics of identified clusters from different regions in France. We also evaluated the use of network information to target prevention efforts. Participants were mostly Caucasian (85.9%) and men (86.7%) who reported sex with men (MSM, 71.4%). Overall, 387 individuals (28.5%) were involved in clusters: 156 patients (11.5%) in 78 dyads and 231 participants (17%) in 42 larger clusters (median size: 4, range 3-41). Compared to individuals with single PHI (n = 969), those in clusters were more frequently men (95.9 vs 83%, p < 0.01), MSM (85.8 vs 65.6%, p < 0.01) and infected with CRF02_AG (20.4 vs 13.4%, p < 0.01). Reconstruction of viral migrations across time suggests that Paris area was the major hub of dissemination of both subtype B and CRF02_AG epidemics. By targeting clustering individuals belonging to the identified active transmission network before 2010, 60 of the 143 onward transmissions could have been prevented.
Conclusion: These analyses support the hypothesis of a recent and rapid rise of CRF02_AG within the French HIV-1 epidemic among MSM. Combined with a short turnaround time for sample processing, targeting prevention efforts based on phylogenetic monitoring may be an efficient way to deliver prevention interventions but would require near real time targeted interventions on the identified index cases and their partners.
Keywords: HIV-1; Phylogeography; Primary infection; Transmission network; Treatment as prevention.
Figures
References
-
- Poon AF, Joy JB, Woods CK, Shurgold S, Colley G, Brumme CJ, et al. The impact of clinical, demographic and risk factors on rates of HIV transmission: a population-based phylogenetic analysis in British Columbia, Canada. J Infect Dis. 2015;211(6):926–935. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu560. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K24 AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101012/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA041007/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MH081482/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AI093163/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI120009/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

