Direct experimental manipulation of intestinal cells in Ascaris suum, with minor influences on the global transcriptome
- PMID: 28223178
- PMCID: PMC5423655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.12.005
Direct experimental manipulation of intestinal cells in Ascaris suum, with minor influences on the global transcriptome
Abstract
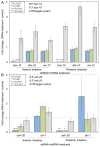
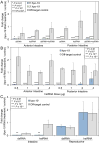
Ascaris suum provides a powerful model for studying parasitic nematodes, including individual tissues such as the intestine, an established target for anthelmintic treatments. Here, we add a valuable experimental component to our existing functional, proteomic, transcriptomic and phylogenomic studies of the Ascaris suum intestine, by developing a method to manipulate intestinal cell functions via direct delivery of experimental treatments (in this case, double-stranded (ds)RNA) to the apical intestinal membrane. We developed an intestinal perfusion method for direct, controlled delivery of dsRNA/heterogeneous small interfering (hsi) RNA into the intestinal lumen for experimentation. RNA-Seq (22 samples) was used to assess influences of the method on global intestinal gene expression. Successful mRNA-specific knockdown in intestinal cells of adult A. suum was accomplished with this new experimental method. Global transcriptional profiling confirmed that targeted transcripts were knocked down more significantly than any others, with only 12 (0.07% of all genes) or 238 (1.3%) off-target gene transcripts consistently differentially regulated by dsRNA treatment or the perfusion experimental design, respectively (after 24h). The system supports controlled, effective delivery of treatments (dsRNA/hsiRNA) to the apical intestinal membrane with relatively minor off-target effects, and builds on our experimental model to dissect A. suum intestinal cell functions with broad relevance to parasitic nematodes.
Keywords: A. suum; Intestine; Methodology; Nematode; RNAi; dsRNA.
Copyright © 2017 Australian Society for Parasitology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Compartmentalization of functions and predicted miRNA regulation among contiguous regions of the nematode intestine.RNA Biol. 2017 Oct 3;14(10):1335-1352. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1166333. Epub 2016 Mar 22. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27002534 Free PMC article.
-
Ascaris suum: RNAi mediated silencing of enolase gene expression in infective larvae.Exp Parasitol. 2011 Jan;127(1):142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.07.019. Epub 2010 Aug 5. Exp Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 20691683
-
Genome-wide tissue-specific gene expression, co-expression and regulation of co-expressed genes in adult nematode Ascaris suum.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Feb 6;8(2):e2678. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002678. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24516681 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: a comparison of the nAChRs of Caenorhabditis elegans and parasitic nematodes.Parasitol Int. 2013 Dec;62(6):606-15. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Parasitol Int. 2013. PMID: 23500392 Review.
-
[Comparative studies on the difference between Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Apr 30;24(2):140-3, 145. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16862915 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Omics Driven Understanding of the Intestines of Parasitic Nematodes.Front Genet. 2019 Jul 25;10:652. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00652. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31402928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defining an optimal control for RNAi experiments with adult Schistosoma mansoni.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 16;13(1):9766. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36826-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37328492 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal cell diversity and treatment responses in a parasitic nematode at single cell resolution.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 4;25(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10203-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38575858 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of the Parasitic Nematode Ascaris and Its Relatives.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 28;12(4):493. doi: 10.3390/genes12040493. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNA pathways in the nematode Ascaris in the absence of piRNAs.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 11;13(1):837. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28482-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35149688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonino de Souza Júnior JD, Ramos Coelho R, Tristan Lourenço I, da Rocha Fragoso R, Barbosa Viana AA, Lima Pepino de Macedo L, Mattar da Silva MC, Gomes Carneiro RM, Engler G, de Almeida-Engler J, Grossi-de-Sa MF. Knocking-Down Meloidogyne incognita Proteases by Plant-Delivered dsRNA Has Negative Pleiotropic Effect on Nematode Vigor. PLoS One. 2014;8:e85364. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barik S. RNAi in moderation. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:796–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

