Active Multienzyme Assemblies for Long-Chain Olefinic Hydrocarbon Biosynthesis
- PMID: 28223313
- PMCID: PMC5388818
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00890-16
Active Multienzyme Assemblies for Long-Chain Olefinic Hydrocarbon Biosynthesis
Abstract
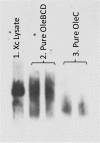
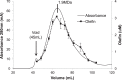
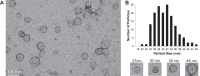
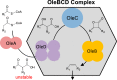
Bacteria from different phyla produce long-chain olefinic hydrocarbons derived from an OleA-catalyzed Claisen condensation of two fatty acyl coenzyme A (acyl-CoA) substrates, followed by reduction and oxygen elimination reactions catalyzed by the proteins OleB, OleC, and OleD. In this report, OleA, OleB, OleC, and OleD were individually purified as soluble proteins, and all were found to be essential for reconstituting hydrocarbon biosynthesis. Recombinant coexpression of tagged OleABCD proteins from Xanthomonas campestris in Escherichia coli and purification over His6 and FLAG columns resulted in OleA separating, while OleBCD purified together, irrespective of which of the four Ole proteins were tagged. Hydrocarbon biosynthetic activity of copurified OleBCD assemblies could be reconstituted by adding separately purified OleA. Immunoblots of nondenaturing gels using anti-OleC reacted with X. campestris crude protein lysate indicated the presence of a large protein assembly containing OleC in the native host. Negative-stain electron microscopy of recombinant OleBCD revealed distinct large structures with diameters primarily between 24 and 40 nm. Assembling OleB, OleC, and OleD into a complex may be important to maintain stereochemical integrity of intermediates, facilitate the movement of hydrophobic metabolites between enzyme active sites, and protect the cell against the highly reactive β-lactone intermediate produced by the OleC-catalyzed reaction.IMPORTANCE Bacteria biosynthesize hydrophobic molecules to maintain a membrane, store carbon, and for antibiotics that help them survive in their niche. The hydrophobic compounds are often synthesized by a multidomain protein or by large multienzyme assemblies. The present study reports on the discovery that long-chain olefinic hydrocarbons made by bacteria from different phyla are produced by multienzyme assemblies in X. campestris The OleBCD multienzyme assemblies are thought to compartmentalize and sequester olefin biosynthesis from the rest of the cell. This system provides additional insights into how bacteria control specific biosynthetic pathways.
Keywords: bacteria; hydrocarbon; multienzyme complex; olefin.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In Vivo Assay Reveals Microbial OleA Thiolases Initiating Hydrocarbon and β-Lactone Biosynthesis.mBio. 2020 Mar 10;11(2):e00111-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00111-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32156808 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and characterization of OleA from Xanthomonas campestris and demonstration of a non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation reaction.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 1;286(13):10930-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.216127. Epub 2011 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21266575 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate Trapping in Crystals of the Thiolase OleA Identifies Three Channels That Enable Long Chain Olefin Biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 23;291(52):26698-26706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.760892. Epub 2016 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27815501 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerance and specificity of polyketide synthases.Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:219-53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.219. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10872449 Review.
-
Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008 Mar;32(2):168-207. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00104.x. Epub 2008 Feb 11. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18266853 Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse hydrocarbon biosynthetic enzymes can substitute for olefin synthase in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-38124-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30718738 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of Long Chain Alkyl Diols and Long Chain Alkenols in Nannochloropsis spp. (Eustigmatophyceae).Plant Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;60(8):1666-1682. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz078. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31058972 Free PMC article.
-
OleA Glu117 is key to condensation of two fatty-acyl coenzyme A substrates in long-chain olefin biosynthesis.Biochem J. 2017 Nov 10;474(23):3871-3886. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170642. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 29025976 Free PMC article.
-
Multimeric structure of a subfamily III haloalkane dehalogenase-like enzyme solved by combination of cryo-EM and x-ray crystallography.Protein Sci. 2023 Oct;32(10):e4751. doi: 10.1002/pro.4751. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37574754 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and diversity of olefins and olefin-biosynthesis genes in Gram-positive bacteria.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020 Apr 15;13:70. doi: 10.1186/s13068-020-01706-y. eCollection 2020. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2020. PMID: 32313552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albro PW, Dittmer JC. 1969. The biochemistry of long-chain nonisoprenoid hydrocarbons. I. Characterization of the hydrocarbons of Sarcina lutea and the isolation of possible intermediates of biosynthesis. Biochemistry 8:394–405. - PubMed
-
- Friedman L, DaCosta B. April 2008. Hydrocarbon-producing genes and methods of their use. International patent WO/2008/147781.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

