Tuberculosis Cutis Orificialis in Adalimumab Related Immunosupressive Patient
- PMID: 28223762
- PMCID: PMC5318510
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.114
Tuberculosis Cutis Orificialis in Adalimumab Related Immunosupressive Patient
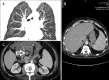
Figures


References
-
- Bravo FG, Gotuzzo E. Cutaneous tuberculosis. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Turkmen M, Turk BG, Kandıloglu G, Dereli T. Tuberculosis cutis orificialis in an immunocompetent patient. Cutis. 2015;95:E4–E6. - PubMed
-
- Dixon WG, Hyrich KL, Watson KD, Lunt M, Galloway J, Ustianowski A, et al. Drug-specific risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register (BSRBR) Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:522–528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohan AK, Coté TR, Block JA, Manadan AM, Siegel JN, Braun MM. Tuberculosis following the use of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:295–299. - PubMed
-
- Wallis RS. Mathematical modeling of the cause of tuberculosis during tumor necrosis factor blockade. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:947–952. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

