Erythrocyte nanovesicles: Biogenesis, biological roles and therapeutic approach: Erythrocyte nanovesicles
- PMID: 28223857
- PMCID: PMC5310160
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.06.010
Erythrocyte nanovesicles: Biogenesis, biological roles and therapeutic approach: Erythrocyte nanovesicles
Abstract
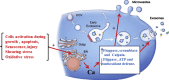
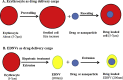
Nanovesicles (NVs) represent a novel transporter for cell signals to modify functions of target cells. Therefore, NVs play many roles in both physiological and pathological processes. This report highlights biogenesis, composition and biological roles of erythrocytes derived nanovesicles (EDNVs). Furthermore, we address utilization of EDNVs as novel drug delivery cargo as well as therapeutic target. EDNVs are lipid bilayer vesicles rich in phospholipids, proteins, lipid raft, and hemoglobin. In vivo EDNVs biogenesis is triggered by an increase of intracellular calcium levels, ATP depletion and under effect of oxidative stress conditions. However, in vitro production of EDNVs can be achieved via hypotonic treatment and extrusion of erythrocyte. NVs can be used as biomarkers for diagnosis, monitoring of therapy and drug delivery system. Many therapeutic agents are suggested to decrease NVs biogenesis.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Erythrocytes; Extracellular vesicles; Nanovesicles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of Red Blood Cell Nanovesicles as a Delivery Tool.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2628:321-336. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2978-9_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36781795
-
Pericyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Mimetic Nanovesicles Restore Erectile Function by Enhancing Neurovascular Regeneration in a Mouse Model of Cavernous Nerve Injury.J Sex Med. 2020 Nov;17(11):2118-2128. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.07.083. Epub 2020 Aug 24. J Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32855091
-
Melatonin Engineered Adipose-Derived Biomimetic Nanovesicles Regulate Mitochondrial Functions and Promote Myocardial Repair in Myocardial Infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Mar 23;9:789203. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.789203. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35402545 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-derived nanovesicles: Promising therapeutics and drug delivery nanoplatforms for brain disorders.Fundam Res. 2023 Dec 5;5(2):830-850. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.09.007. eCollection 2025 Mar. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 40242551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanovesicles derived from edible plants: a new player that contributes to the function of foods.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2025 Jan 24;89(2):179-186. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbae198. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39730148 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid insertion enables targeted functionalization of paclitaxel-loaded erythrocyte membrane nanosystem by tumor-penetrating bispecific recombinant protein.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Sep 11;13:5347-5359. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S165109. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30254439 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Drug Delivery: A Focus on Red Blood Cells-Derived EVs.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 21;15(2):365. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020365. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Erythrocyte microRNAs show biomarker potential and implicate multiple sclerosis susceptibility genes.Clin Transl Med. 2020 Jan;10(1):74-90. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.22. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Clin Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32508012 Free PMC article.
-
From Molecular Therapies to Lysosomal Transplantation and Targeted Drug Strategies: Present Applications, Limitations, and Future Prospects of Lysosomal Medications.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 24;15(3):327. doi: 10.3390/biom15030327. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red Blood Cell Membrane Vesicles for siRNA Delivery: A Biocompatible Carrier With Passive Tumor Targeting and Prolonged Plasma Residency.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 15;20:3269-3301. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S504644. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40109366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- EL Andaloussi S., Mäger I., Mäger X.O., Wood M.J. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013;12(5):347–357. - PubMed
-
- Antwi-Baffour S., Nyarkoah A.W., Kyeremeh R., Abdulai S.M. Plasma membrane-derived vesicles in sickle cell disease: a possible indicator of the continuous endothelial stimulation and/or injury to blood cells. Amer. J. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013;1(4):99–102.
-
- Antwi-Baffour S., Boafo A.O., Kyeremeh R., Mahmood S.A. Plasma Membrane-derived Vesicles (PMVs) in G6PD Deficient Patients. SOJ Immunol. 2013;1(1):4.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

