Chitosan treatment abrogates hypercholesterolemia-induced erythrocyte's arginase activation
- PMID: 28223872
- PMCID: PMC5310152
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.05.007
Chitosan treatment abrogates hypercholesterolemia-induced erythrocyte's arginase activation
Abstract
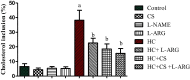
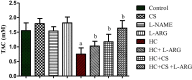
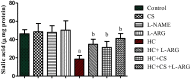
This study aimed to evaluate the protective effect of chitosan (CS) against hypercholesterolemia (HC) induced arginase activation and disruption of nitric oxide (NO) biosynthesis using erythrocytes as cellular model. Human erythrocytes were isolated and classified into eight groups. Next, cells were treated with l-arginine (l-ARG), Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME), CS or CS + l-ARG in the presence of normal plasma or cholesterol enriches plasma. Then, erythrocytes were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The present results revealed that, HC induced significant increase of cholesterol inclusion into erythrocytes membrane compared to control. Moreover, HC caused significant decrease in nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity similar to l-NAME; however, arginase activity and arginase/NOS ratio significantly increased compared to control. On contrast, treatment of HC with, l-arginine, CS or CS plus l-arginine prevents HC induced cholesterol loading into erythrocytes membrane, NOS inhibition and arginase activation. This study suggested that CS could be protective agent against HC induced disruption of erythrocyte's oxidative status and arginase activation.
Keywords: Arginase; Chitosan; Erythrocytes; Hypercholesterolemia; Nitric oxide.
Figures
References
-
- Denny P.C., Denny P.A., Allerton S.E. Determination of sialic acid using 2-thiobarbituric acid in the absence of hazardous sodium arsenite. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1983;131:333–336. - PubMed
-
- Devrim E., Ergüder I.B., Ozbek H., Durak I. High-cholesterol diet increases xanthine oxidase and decreases nitric oxide synthase activities in erythrocytes from rats. Nutr. Res. 2008;28(3):212–215. - PubMed
-
- Fan W., Yan W., Xu Z., Ni H. Erythrocytes load of low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles as a potential vascular drug delivery system. Colloids Surf. B. 2012;95:258–265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

