1H NMR spectra dataset and solid-state NMR data of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)
- PMID: 28224130
- PMCID: PMC5310203
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2017.01.013
1H NMR spectra dataset and solid-state NMR data of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)
Abstract
In this article the NMR data from chemical shifts, coupling constants, and structures of all the characterized compounds were provided, beyond a complementary PCA evaluation for the corresponding manuscript (E.G. Alves Filho, L.M.A. Silva, E.M. Teofilo, F.H. Larsen, E.S. de Brito, 2017) [3]. In addition, a complementary assessment from solid-state NMR data was provided. For further chemometric analysis, numerical matrices from the raw 1H NMR data were made available in Microsoft Excel workbook format (.xls).
Keywords: 1H qNMR; CP-MAS; Chemometrics; Cowpea seeds; SP/MAS.
Figures

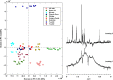
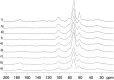
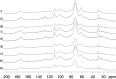
References
-
- Alves Filho E.G., Almeida F.D.L., Cavalcante R.S., de Brito E.S., Cullen P.J., Frias J.M., Bourke P., Fernandes F.A.N., Rodrigues S. 1H NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics evaluation of non-thermal processing of orange juice. Food Chem. 2016;204:102–107. - PubMed
-
- Alves Filho E.G., Silva L.M.A., Choze R., Lião L.M., Honda N.K., Alcantara G.B. Discrimination of sugarcane according to cultivar by 1H NMR and chemometric analyses. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012;23:273–279.
-
- Balayssac S., Trefi S., Gilard V., Malet-Martino M., Martino R., Delsuc M.A. 2D and 3D DOSY 1H NMR, a useful tool for analysis of complex mixtures: application to herbal drugs or dietary supplements for erectile dysfunction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009;50:602–612. - PubMed
-
- Boffo E.F., Tavares L.A., Ferreira M.M.C., Ferreira A.G. Classification of Brazilian vinegars according to their 1H NMR spectra by pattern recognition analysis, LWT. Food Sci. Technol. 2009;42:1455–1460.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

