The Role of Body Weight on Bone in Anorexia Nervosa: A HR-pQCT Study
- PMID: 28224178
- PMCID: PMC5486942
- DOI: 10.1007/s00223-017-0254-7
The Role of Body Weight on Bone in Anorexia Nervosa: A HR-pQCT Study
Abstract
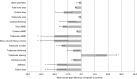
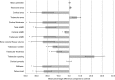
Anorexia nervosa (AN) is associated with decreased bone mineral density and increased risk of fracture. The aim of this study was to assess bone geometry, volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), trabecular microarchitecture and estimated failure load in weight-bearing vs. non-weight-bearing bones in AN. We included twenty-five females with AN, and twenty-five female controls matched on age and height. Bone geometry, vBMD and trabecular microarchitecture were assessed using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography of the distal radius and tibia. At both sites, cortical perimeter and total bone area were similar in patients and controls. Total vBMD was lower in the AN group in the tibia (p < 0.0005) but not in the radius. In the tibia, cortical thickness was approximately 25% lower (p < 0.0005) in the AN group, whereas there was no significant difference in the radius. In terms of trabecular microarchitecture, all indices [bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV); trabecular thickness (Tb.Th.), trabecular number (Tb.N) and trabecular spacing (Tb.Sp.)] were impaired in AN in the tibia (p values range < 0.01-0.0001). In the radius, BV/TV and Tb.N were lower (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively); Tb.Sp. was higher (p < 0.001), whereas Tb.Th. did not differ, compared to controls. Estimated failure load was lower in patients in both the radius and the tibia (p < 0.0005 and p < 0.0001, respectively), most pronounced in the tibia. In conclusion, the impairment of cortical thickness and estimated failure load were significantly more pronounced in the weight-bearing tibia, compared to the non-weight-bearing radius, implying a direct effect of low body weight on bone loss in AN.
Keywords: Anorexia nervosa; Bone geometry; Bone microarchitecture; High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography; Mechanical loading.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
René K. Støving has received lecture fees from Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly and Company. Authors Jacob Frølich, Stinus Hansen, Laura Al-Dakhiel Winkler, Andreas K. Andresen, Anne Pernille Hermann, and René K. Støving declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All subjects signed a written form of consent, and the study was approved by the local ethics review board (No. S-2010002).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

