The EXERRT trial: "EXErcise to Regadenoson in Recovery Trial": A phase 3b, open-label, parallel group, randomized, multicenter study to assess regadenoson administration following an inadequate exercise stress test as compared to regadenoson without exercise for myocardial perfusion imaging using a SPECT protocol
- PMID: 28224449
- PMCID: PMC5491644
- DOI: 10.1007/s12350-017-0813-3
The EXERRT trial: "EXErcise to Regadenoson in Recovery Trial": A phase 3b, open-label, parallel group, randomized, multicenter study to assess regadenoson administration following an inadequate exercise stress test as compared to regadenoson without exercise for myocardial perfusion imaging using a SPECT protocol
Abstract
Background: This study assessed the non-inferiority and safety of regadenoson administration during recovery from inadequate exercise compared with administration without exercise.
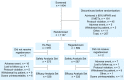
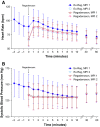
Methods: Patients unable to achieve adequate exercise stress were randomized to regadenoson 0.4 mg either during recovery (Ex-Reg) or 1 hour after inadequate exercise (Regadenoson) (MPI1). All patients also underwent non-exercise regadenoson MPI 1-14 days later (MPI2). The number of segments with reversible perfusion defects (RPDs) detected using single photon emission computerized tomography imaging was categorized. The primary analysis evaluated the majority agreement rate between Ex-Reg and Regadenoson groups.
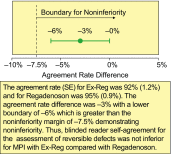
Results: 1,147 patients were randomized. The lower bound of the 95% confidence interval of the difference in agreement rates (-6%) was above the -7.5% non-inferiority margin, demonstrating non-inferiority of Ex-Reg to Regadenoson. Adverse events were numerically less with Ex-Reg (MPI1). In the Ex-Reg group, one patient developed an acute coronary syndrome and another had a myocardial infarction following regadenoson after exercise. Upon review, both had electrocardiographic changes consistent with ischemia prior to regadenoson.
Conclusions: Administering regadenoson during recovery from inadequate exercise results in comparable categorization of segments with RPDs and with careful monitoring appears to be well tolerated in patients without signs/symptoms of ischemia during exercise and recovery.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01618669.
Keywords: Exercise; myocardial perfusion imaging; pharmacologic stress; regadenoson; vasodilator stress.
Figures

Comment in
-
The interface of emotion and biology in myocardial ischemia: Can we progress using the traditional paradigm?J Nucl Cardiol. 2017 Jun;24(3):783-787. doi: 10.1007/s12350-016-0762-2. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Nucl Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28155190 No abstract available.
-
Regadenoson stress during low-level exercise: The EXERRT trial-does it move the needle?J Nucl Cardiol. 2017 Jun;24(3):803-808. doi: 10.1007/s12350-017-0873-4. Epub 2017 May 15. J Nucl Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28508268 No abstract available.
References
-
- Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Hansen CL, Taillefer R, Yao S-S. ASNC imaging guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures: Stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Ahlberg AW, Baghdasarian SB, Athar H, Thompsen JP, Katten DM, Noble GL, et al. Symptom-limited exercise combined with dipyridamole stress: Prognostic value in assessment of known or suspected coronary artery disease by use of gated SPECT imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2008;15:42–56. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclcard.2007.09.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holly TA, Satran A, Bromet DS, Mieres JH, Frey MJ, Elliott MD, et al. The impact of adjunctive adenosine infusion during exercise myocardial perfusion imaging: Results of the Both Exercise and Adenosine Stress Test (BEAST) trial. J Nucl Cardiol. 2003;10:291–296. doi: 10.1016/S1071-3581(02)43236-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

