Genetic risk variants for social anxiety
- PMID: 28224735
- PMCID: PMC5325045
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32520
Genetic risk variants for social anxiety
Erratum in
-
Genetic risk variants for social anxiety.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Jun;174(4):470-482. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32541. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28512750 No abstract available.
Corrected and republished in
-
Genetic risk variants for social anxiety.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017 Jun;174(4):470-482. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32541. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28512750 No abstract available.
Abstract
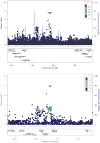
Social anxiety is a neurobehavioral trait characterized by fear and reticence in social situations. Twin studies have shown that social anxiety has a heritable basis, shared with neuroticism and extraversion, but genetic studies have yet to demonstrate robust risk variants. We conducted genomewide association analysis (GWAS) of subjects within the Army Study To Assess Risk and Resilience in Servicemembers (Army STARRS) to (i) determine SNP-based heritability of social anxiety; (ii) discern genetic risk loci for social anxiety; and (iii) determine shared genetic risk with neuroticism and extraversion. GWAS were conducted within ancestral groups (EUR, AFR, LAT) using linear regression models for each of the three component studies in Army STARRS, and then meta-analyzed across studies. SNP-based heritability for social anxiety was significant (h2g = 0.12, P = 2.17 × 10-4 in EUR). One meta-analytically genomewide significant locus was seen in each of EUR (rs708012, Chr 6: BP 36965970, P = 1.55 × 10-8 ; beta = 0.073) and AFR (rs78924501, Chr 1: BP 88406905, P = 3.58 × 10-8 ; beta = 0.265) samples. Social anxiety in Army STARRS was significantly genetically correlated (negatively) with extraversion (rg = -0.52, se = 0.22, P = 0.02) but not with neuroticism (rg = 0.05, se = 0.22, P = 0.81) or with an anxiety disorder factor score (rg = 0.02, se = 0.32, P = 0.94) from external GWAS meta-analyses. This first GWAS of social anxiety confirms a genetic basis for social anxiety, shared with extraversion but possibly less so with neuroticism. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: anxiety; extraversion; neuroticism; social anxiety; social phobia.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Arbelle S, Benjamin J, Golin M, Kremer I, Belmaker RH, Ebstein RP. Relation of shyness in grade school children to the genotype for the long form of the serotonin transporter promoter region polymorphism. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160(4):671–676. - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu OJ, Hettema JM, Neale MC, Prescott CA, Kendler KS. Low extraversion and high neuroticism as indices of genetic and environmental risk for social phobia, agoraphobia, and animal phobia. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164(11):1714–1721. - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu OJ, Samuels JF, Costa PT, Reti IM, Eaton WW, Nestadt G. Anxiety and depressive disorders and the five-factor model of personality: a higher- and lower-order personality trait investigation in a community sample. Depress Anxiety. 2004;20(2):92–97. - PubMed
-
- Bulik-Sullivan B, Finucane HK, Anttila V, Gusev A, Day FR, Loh PR, Duncan L, Perry JR, Patterson N, Robinson EB, Daly MJ, Price AL, Neale BM ReproGen C, Psychiatric Genomics C, Genetic Consortium for Anorexia Nervosa of the Wellcome Trust Case Control C. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat Genet. 2015;47(11):1236–1241. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

