Genomewide Association Study of Alcohol Dependence Identifies Risk Loci Altering Ethanol-Response Behaviors in Model Organisms
- PMID: 28226201
- PMCID: PMC5404949
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.13362
Genomewide Association Study of Alcohol Dependence Identifies Risk Loci Altering Ethanol-Response Behaviors in Model Organisms
Abstract
Background: Alcohol dependence (AD) shows evidence for genetic liability, but genes influencing risk remain largely unidentified.
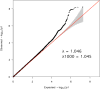
Methods: We conducted a genomewide association study in 706 related AD cases and 1,748 unscreened population controls from Ireland. We sought replication in 15,496 samples of European descent. We used model organisms (MOs) to assess the role of orthologous genes in ethanol (EtOH)-response behaviors. We tested 1 primate-specific gene for expression differences in case/control postmortem brain tissue.
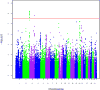
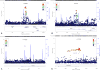
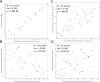
Results: We detected significant association in COL6A3 and suggestive association in 2 previously implicated loci, KLF12 and RYR3. None of these signals are significant in replication. A suggestive signal in the long noncoding RNA LOC339975 is significant in case:control meta-analysis, but not in a population sample. Knockdown of a COL6A3 ortholog in Caenorhabditis elegans reduced EtOH sensitivity. Col6a3 expression correlated with handling-induced convulsions in mice. Loss of function of the KLF12 ortholog in C. elegans impaired development of acute functional tolerance (AFT). Klf12 expression correlated with locomotor activation following EtOH injection in mice. Loss of function of the RYR3 ortholog reduced EtOH sensitivity in C. elegans and rapid tolerance in Drosophila. The ryanodine receptor antagonist dantrolene reduced motivation to self-administer EtOH in rats. Expression of LOC339975 does not differ between cases and controls but is reduced in carriers of the associated rs11726136 allele in nucleus accumbens (NAc).
Conclusions: We detect association between AD and COL6A3, KLF12, RYR3, and LOC339975. Despite nonreplication of COL6A3, KLF12, and RYR3 signals, orthologs of these genes influence behavioral response to EtOH in MOs, suggesting potential involvement in human EtOH response and AD liability. The associated LOC339975 allele may influence gene expression in human NAc. Although the functions of long noncoding RNAs are poorly understood, there is mounting evidence implicating these genes in multiple brain functions and disorders.
Keywords: COL6A3; KLF12; LOC339975; RYR3; Alcohol Dependence.
Copyright © 2017 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Ridinger received compensation from Lundbeck Switzerland and the Lundbeck Institute for advisory boards and expert meetings, and from Lundbeck and Lilly Suisse for workshops and presentations. N. Wodarz has received speaker’s honoraria and travel funds from Janssen-Cilag and Essex Pharma. He took part in industry sponsored multi-center randomized trials by D&A Pharma and Lundbeck. H. R. Kranzler has been a consultant or advisory board member for Alkermes, Lilly, Lundbeck, Pfizer, and Roche. He is also a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which is supported by AbbVie, Alkermes, Ethypharm, Lilly, Lundbeck, and Pfizer. Except as noted above, all other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Atsma F, Veldhuizen I, de Vegt F, Doggen C, de Kort W. Cardiovascular and demographic characteristics in whole blood and plasma donors: results from the Donor InSight study. Transfusion. 2011;51:412–420. - PubMed
-
- Aulchenko YS, Ripke S, Isaacs A, van Duijn CM. GenABEL: an R library for genome-wide association analysis. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1294–1296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AA022749/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 AA017828/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD010440/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA016667/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AA021399/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R28 AA012725/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA016837/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020634/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA022537/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AA018755/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA011408/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083094/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AA011408/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

