Structural basis for the hijacking of endosomal sorting nexin proteins by Chlamydia trachomatis
- PMID: 28226239
- PMCID: PMC5348129
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.22311
Structural basis for the hijacking of endosomal sorting nexin proteins by Chlamydia trachomatis
Abstract
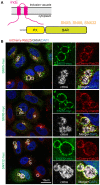
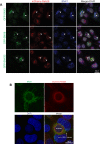
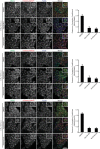
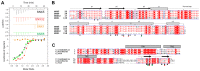
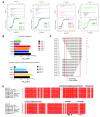
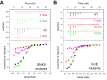
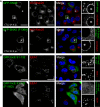
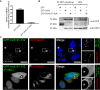
During infection chlamydial pathogens form an intracellular membrane-bound replicative niche termed the inclusion, which is enriched with bacterial transmembrane proteins called Incs. Incs bind and manipulate host cell proteins to promote inclusion expansion and provide camouflage against innate immune responses. Sorting nexin (SNX) proteins that normally function in endosomal membrane trafficking are a major class of inclusion-associated host proteins, and are recruited by IncE/CT116. Crystal structures of the SNX5 phox-homology (PX) domain in complex with IncE define the precise molecular basis for these interactions. The binding site is unique to SNX5 and related family members SNX6 and SNX32. Intriguingly the site is also conserved in SNX5 homologues throughout evolution, suggesting that IncE captures SNX5-related proteins by mimicking a native host protein interaction. These findings thus provide the first mechanistic insights both into how chlamydial Incs hijack host proteins, and how SNX5-related PX domains function as scaffolds in protein complex assembly.
Keywords: Chlamydia trachomatis; biophysics; chlamydial inclusion; endosome; human; infectious disease; membrane transport; microbiology; sorting nexin; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Jain S, Kapral GJ, Grosse Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner RD, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. The Phenix software for automated determination of macromolecular structures. Methods. 2011;55:94–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.07.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aeberhard L, Banhart S, Fischer M, Jehmlich N, Rose L, Koch S, Laue M, Renard BY, Schmidt F, Heuer D. The proteome of the isolated Chlamydia trachomatis containing vacuole reveals a complex trafficking platform enriched for retromer components. PLOS Pathogens. 2015;11:e1004883. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004883. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aral SO, Over M, Manhart L, Holmes KK. Sexually Transmitted Infections. In: Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, Jha P, Mills A, Musgrove P, editors. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. Washington DC: Oxford University Press; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

