Weight-loss and exercise for communities with arthritis in North Carolina (we-can): design and rationale of a pragmatic, assessor-blinded, randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28228115
- PMCID: PMC5322619
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-017-1441-4
Weight-loss and exercise for communities with arthritis in North Carolina (we-can): design and rationale of a pragmatic, assessor-blinded, randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Recently, we determined that in a rigorously monitored environment an intensive diet-induced weight loss of 10% combined with exercise was significantly more effective at reducing pain in men and women with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) than either intervention alone. Compared to previous long-term weight loss and exercise trials of knee OA, our intensive diet-induced weight loss and exercise intervention was twice as effective at reducing pain intensity. Whether these results can be generalized to less intensively monitored cohorts is unknown. Thus, the policy relevant and clinically important question is: Can we adapt this successful solution to a pervasive public health problem in real-world clinical and community settings? This study aims to develop a systematic, practical, cost-effective diet-induced weight loss and exercise intervention implemented in community settings and to determine its effectiveness in reducing pain and improving other clinical outcomes in persons with knee OA.
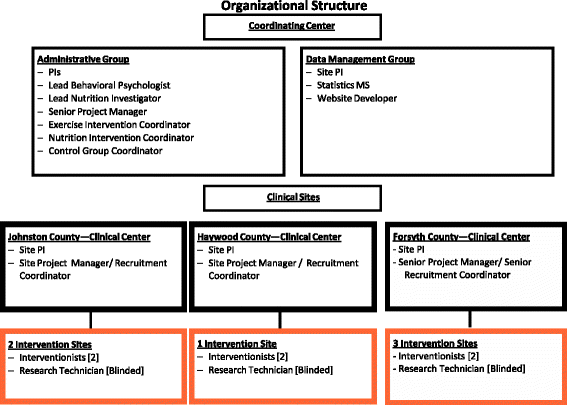
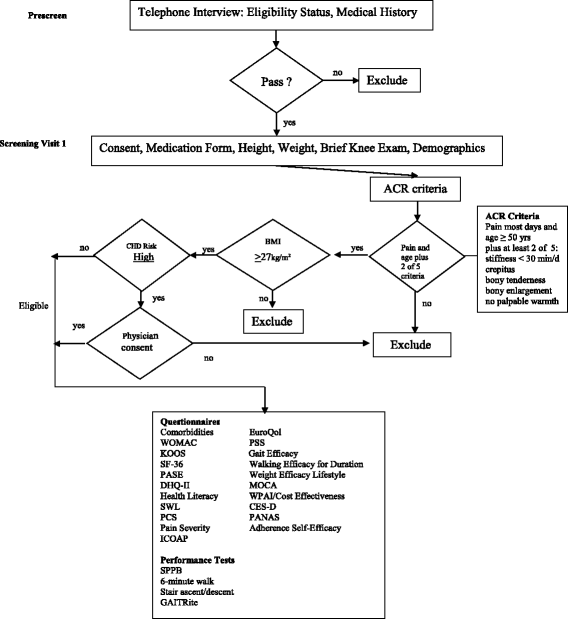
Methods/design: This is a Phase III, pragmatic, assessor-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Participants will include 820 ambulatory, community-dwelling, overweight and obese (BMI ≥ 27 kg/m2) men and women aged ≥ 50 years who meet the American College of Rheumatology clinical criteria for knee OA. The primary aim is to determine whether a community-based 18-month diet-induced weight loss and exercise intervention based on social cognitive theory and implemented in three North Carolina counties with diverse residential (from urban to rural) and socioeconomic composition significantly decreases knee pain in overweight and obese adults with knee OA relative to a nutrition and health attention control group. Secondary aims will determine whether this intervention improves self-reported function, health-related quality of life, mobility, and is cost-effective.
Discussion: Many physicians who treat people with knee OA have no practical means to implement weight loss and exercise treatments as recommended by numerous OA treatment guidelines. This study will establish the effectiveness of a community program that will serve as a blueprint and exemplar for clinicians and public health officials in urban and rural communities to implement a diet-induced weight loss and exercise program designed to reduce knee pain and improve other clinical outcomes in overweight and obese adults with knee OA.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT02577549 October 12, 2015.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Community based research; Knee pain; Osteoarthritis; Pragmatic.
Figures

References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability [YLDs] for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2163–96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

