[Measurements of Pulmonary Artery Size for Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Clinical Application]
- PMID: 28228220
- PMCID: PMC5972974
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.02.10
[Measurements of Pulmonary Artery Size for Assessment of Pulmonary Hypertension by Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance and Clinical Application]
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) often leads to dilatation of main pulmonary artery (MPA). MPA measurements can be used to predict PH. This aim of this study is to investigate power of MPA vessel indices, which are acquired from cardiovascular magnetic resonance, to evaluate PH.
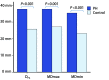
Methods: Cardiovascular-magnetic-resonance-determined parameters of MPA were acquired and calculated in 83 PH patients, whose diagnosis were confirmed with right heart catheterization and 49 healthy volunteers; these parameters included MPA diameter (DPA), ratio of DPA and ascending aorta diameter (DPA/DAo), max mean diameter (MDmax), min mean diameter (MDmin), fraction transverse diameter (fTD), fraction longitudinal diameter (fLD), and distensibility.
Results: Compared with control group, DPA, DPA/DAo, MDmax, and MDmin were significantly higher in patients with PH (P<0.001); fTD, fLD, and distensibility significantly decreased (P<0.001). fTD was lesser than fLD in control group (P<0.001), whereas difference was not observed in PH (P=0.305). MPA indices were significantly correlated with mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) (P<0.05), and strongest correlation was observed for DPA/DAo (r=0.534, P<0.001). By receiver operating characteristic analysis, MDmin>28.4 mm, and MDmax>32.4 mm (area under the curve, AUC=0.979, 0.981) showed best performance in predicting PH, yielding highest specificity at 100%.
Conclusions: Noninvasive cardiovascular-magnetic-resonance-derived MPA measurements provide excellent and practical reference in clinical settings for detecting PH.
背景与目的 肺高血压(pulmonary hypertension, PH)将导致主肺动脉扩张,主肺动脉(main pulmonary artery, MPA)径线测量可被临床用于评估PH。本研究旨在探讨心血管磁共振(cardiovascular magnetic resonance, CMR)测量MPA各径线参数评价PH的价值。方法 对经右心导管检查(right heart catheterization, RHC)确诊的83例PH患者及49例健康志愿者CMR图像进行分析,测量和计算主肺动脉横径(main pulmonary artery diameter, DPA)、DPA与升主动脉横径之比(the ratio of DPA and ascending aorta diameter, DPA/DAo)、最大平均直径(max mean diameter, MDmax)、最小平均直径(min mean diameter, MDmin)、横径变化分数(fraction transverse diameter, fTD)、纵径变化分数(fraction longitudinal diameter, fLD)及MPA顺应性。结果 PH组的DPA、DPA/DAo、MDmax、MDmin明显增大(P<0.001),fTD、fLD、顺应性显著减低(P<0.001)。对照组fTD小于fLD(P<0.001),但PH组两参数无明显差异(P=0.305)。MPA各径线参数均与平均肺动脉压(mean pulmonary arterial pressure, mPAP)显著相关(P<0.05),以DPA/DAo的相关性(r=0.534, P<0.001)最强。ROC曲线分析表明MDmin>28.4 mm和MDmax>32.4 mm预测PH的效能更高[曲线下面积(area under the curve, AUC=0.979, 0.981)],并且两者的特异性均达100%。结论 CMR无创性测量MPA径线评价PH具有临床实用价值。.
Figures




References
-
- Gali EN, Humbert M, Vachiery J, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the joint task force for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension of the european society of cardiology (ESC) and the european respiratory society (ERS): endorsed by: association for european paediatric and congenital cardiology (AEPC), international society for heart and lung transplantation (ISHLT) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26320113 Eur Heart J. 2015;46(4):903–975. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

