Current Concepts on the Physiopathological Relevance of Dopaminergic Receptors
- PMID: 28228718
- PMCID: PMC5296367
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00027
Current Concepts on the Physiopathological Relevance of Dopaminergic Receptors
Abstract
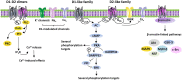
Dopamine (DA) is a key neurotransmitter modulating essential functions of the central nervous system (CNS), like voluntary movement, reward, several cognitive functions and goal-oriented behaviors. The factual relevance of DAergic transmission can be well appreciated by considering that its dysfunction is recognized as a core alteration in several devastating neurological and psychiatric disorders, including Parkinson's disease (PD) and associated movement disorders, as well as, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and addiction. Here we present an overview of the current knowledge on the involvement of DAergic receptors in the regulation of key physiological brain activities, and the consequences of their dysfunctions in brain disorders such as PD, schizophrenia and addiction.
Keywords: DAergic receptors; dopamine; mesocortical pathway; mesolimbic pathway; nigrostriatal pathway.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

