Molecular and Functional Characterization of Wheat ARGOS Genes Influencing Plant Growth and Stress Tolerance
- PMID: 28228774
- PMCID: PMC5296299
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00170
Molecular and Functional Characterization of Wheat ARGOS Genes Influencing Plant Growth and Stress Tolerance
Abstract
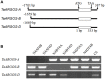
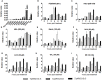
Auxin Regulated Gene involved in Organ Size (ARGOS) is significantly and positively associated with organ size and is involved in abiotic stress responses in plants. However, no studies on wheat ARGOS genes have been reported to date. In the present study, three TaARGOS homoeologous genes were isolated and located on chromosomes 4A, 4B, and 4D of bread wheat, all of which are highly conserved in wheat and its wild relatives. Comparisons of gene expression in different tissues demonstrated that the TaARGOSs were mainly expressed in the stem. Furthermore, the TaARGOS transcripts were significantly induced by drought, salinity, and various phytohormones. Transient expression of the TaARGOS-D protein in wheat protoplasts showed that TaARGOS-D localized to the endoplasmic reticulum. Moreover, overexpression of TaARGOS-D in Arabidopsis resulted in an enhanced germination rate, larger rosette diameter, increased rosette leaf area, and higher silique number than in wild-type (WT) plants. The roles of TaARGOS-D in the control of plant growth were further studied via RNA-seq, and it was found that 105 genes were differentially expressed; most of these genes were involved in 'developmental processes.' Interestingly, we also found that overexpression of TaARGOS-D in Arabidopsis improved drought and salinity tolerance and insensitivity to ABA relative to that in WT plants. Taken together, these results demonstrate that the TaARGOSs are involved in seed germination, seedling growth, and abiotic stress tolerance.
Keywords: ABA; Arabidopsis; TaARGOS; abiotic stress; transgenic gene; wheat.
Figures








References
-
- Andriankaja M. E., Danisman S., Mignolet-Spruyt L. F., Claeys H., Kochanke I., Vermeersch M., et al. (2014). Transcriptional coordination between leaf cell differentiation and chloroplast development established by TCP20 and the subgroup Ib bHLH transcription factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 85 233–245. 10.1007/s11103-014-0180-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fabre D., Adriani D. E., Dingkuhn M., Ishimaru T., Punzalan B., Lafarge T., et al. (2016). The qTSN4 effect on flag leaf size, photosynthesis and panicle size, benefits to plant grain production in rice, depending on light availability. Front. Plant Sci. 7:623 10.3389/fpls.2016.00623 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

