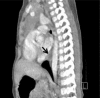
An Unusual Cause of Pediatric Dysphagia: Bronchogenic Cyst
- PMID: 28229098
- PMCID: PMC5308433
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X16686492
An Unusual Cause of Pediatric Dysphagia: Bronchogenic Cyst
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Turkyilmaz A, Eroglu A, Subasi M, Findi G. Intramural esophageal bronchogenic cyst: a review of the literature. Dis Esophagus. 2007;20:461-465. - PubMed
-
- Hyman SL, Porter CA, Page TJ, Iwata BA, Kissel R, Batshaw ML. Behavior management of feeding disturbances in urea cycle and organic acid disorders. J Pediatr. 1987;111:558-562. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph CD, Link DT. Feeding disorders in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002;49:97-112. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph CD, Mazur LJ, Werlin SL, et al. Guidelines for evaluation and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in infants and children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001;32(suppl 2):S1-S31. - PubMed
-
- St-Georges R, Deslauriers J, Duranceau A, et al. Clinical spectrum of bronchogenic cysts of the mediastinum and lung in the adult. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991;52:6-13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

