Probing the Molecular Mechanism of Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation by NO in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 28230071
- PMCID: PMC5322342
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43112
Probing the Molecular Mechanism of Human Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Activation by NO in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
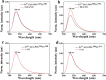
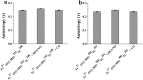
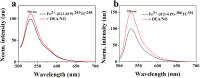
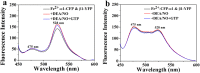
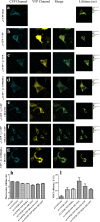
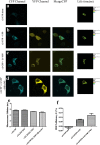
Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is a heme-containing metalloprotein in NO-sGC-cGMP signaling. NO binds to the heme of sGC to catalyze the synthesis of the second messenger cGMP, which plays a critical role in several physiological processes. However, the molecular mechanism for sGC to mediate the NO signaling remains unclear. Here fluorophore FlAsH-EDT2 and fluorescent proteins were employed to study the NO-induced sGC activation. FlAsH-EDT2 labeling study revealed that NO binding to the H-NOX domain of sGC increased the distance between H-NOX and PAS domain and the separation between H-NOX and coiled-coil domain. The heme pocket conformation changed from "closed" to "open" upon NO binding. In addition, the NO-induced conformational change of sGC was firstly investigated in vivo through fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy. The results both in vitro and in vivo indicated the conformational change of the catalytic domain of sGC from "open" to "closed" upon NO binding. NO binding to the heme of H-NOX domain caused breaking of Fe-N coordination bond, initiated the domain moving and conformational change, induced the allosteric effect of sGC to trigger the NO-signaling from H-NOX via PAS &coiled-coil to the catalytic domain, and ultimately stimulates the cyclase activity of sGC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Derbyshire E. R. & Marletta M. A. Structure and regulation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Annual review of biochemistry 81, 533–559 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Munzel T. et al. Physiology and pathophysiology of vascular signaling controlled by guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate-dependent protein kinase [corrected]. Circulation 108, 2172–2183 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Warner T. D., Mitchell J. A., Sheng H. & Murad F. Effects of cyclic GMP on smooth muscle relaxation. Advances in pharmacology (San Diego, Calif.) 26, 171–194 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Sanders K. M. et al. Nitric oxide as a non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic neurotransmitter in the gastrointestinal tract. Jpn J Pharmacol 58 Suppl 2, 220P–225P (1992). - PubMed
-
- Zhong F., Wang H., Ying T., Huang Z. X. & Tan X. Efficient expression of human soluble guanylate cyclase in Escherichia coli and its signaling-related interaction with nitric oxide. Amino acids 39, 399–408 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

