Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients display an altered lipoprotein profile with dysfunctional HDL
- PMID: 28230201
- PMCID: PMC5322497
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43410
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients display an altered lipoprotein profile with dysfunctional HDL
Abstract
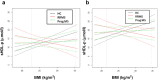
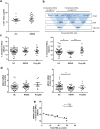
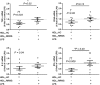
Lipoproteins modulate innate and adaptive immune responses. In the chronic inflammatory disease multiple sclerosis (MS), reports on lipoprotein level alterations are inconsistent and it is unclear whether lipoprotein function is affected. Using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, we analysed the lipoprotein profile of relapsing-remitting (RR) MS patients, progressive MS patients and healthy controls (HC). We observed smaller LDL in RRMS patients compared to healthy controls and to progressive MS patients. Furthermore, low-BMI (BMI ≤ 23 kg/m2) RRMS patients show increased levels of small HDL (sHDL), accompanied by larger, triglyceride (TG)-rich VLDL, and a higher lipoprotein insulin resistance (LP-IR) index. These alterations coincide with a reduced serum capacity to accept cholesterol via ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter G1, an impaired ability of HDL3 to suppress inflammatory activity of human monocytes, and modifications of HDL3's main protein component ApoA-I. In summary, lipoprotein levels and function are altered in RRMS patients, especially in low-BMI patients, which may contribute to disease progression in these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Barter P. J. et al.. Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circulation research 95, 764–772 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Hyka N. et al.. Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits the production of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by blocking contact-mediated activation of monocytes by T lymphocytes. Blood 97, 2381–2389 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Murphy A. J. et al.. High-density lipoprotein reduces the human monocyte inflammatory response. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28, 2071–2077 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Movva R. & Rader D. J. Laboratory assessment of HDL heterogeneity and function. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 67, 7–21 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

