Multinational outbreak of travel-related Salmonella Chester infections in Europe, summers 2014 and 2015
- PMID: 28230522
- PMCID: PMC5322187
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.7.30463
Multinational outbreak of travel-related Salmonella Chester infections in Europe, summers 2014 and 2015
Abstract
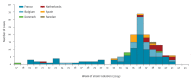
Between 2014 and 2015, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control was informed of an increase in numbers of Salmonella enterica serotype Chester cases with travel to Morocco occurring in six European countries. Epidemiological and microbiological investigations were conducted. In addition to gathering information on the characteristics of cases from the different countries in 2014, the epidemiological investigation comprised a matched case-case study involving French patients with salmonellosis who travelled to Morocco that year. A univariate conditional logistic regression was performed to quantify associations. The microbiological study included a whole genome sequencing (WGS) analysis of clinical and non-human isolates of S. Chester of varied place and year of isolation. A total of 162 cases, mostly from France, followed by Belgium, the Netherlands, Spain, Denmark and Sweden were reported, including 86 (53%) women. The median age per country ranged from 3 to 38 years. Cases of S. Chester were more likely to have eaten in a restaurant and visited the coast of Morocco. The results of WGS showed five multilocus sequence types (ST), with 96 of 153 isolates analysed clustering into a tight group that corresponded to a novel ST, ST1954. Of these 96 isolates, 46 (48%) were derived from food or patients returning from Morocco and carried two types of plasmids containing either qnrS1 or qnrB19 genes. This European-wide outbreak associated with travel to Morocco was likely a multi-source outbreak with several food vehicles contaminated by multidrug-resistant S. Chester strains.
Keywords: Morocco; Salmonella; WGS; case-case study; outbreak; serotype Chester.
This article is copyright of The Authors, 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Gossner CM, de Jong B, Hoebe CJ, Coulombier D, European Food and Waterborne Diseases Study Group . Event-based surveillance of food- and waterborne diseases in Europe: urgent inquiries (outbreak alerts) during 2008 to 2013. Euro Surveill. 2015;20(25):21166. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES2015.20.25.21166 - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), 2015. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J. 2015;13(1):3991 Available from: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/efsajournal/pub/3991
-
- Grimont PAD, Weill FX. Antigenic formulae of the Salmonella serovars, 9th ed. Paris, France: WHO Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella, Institut Pasteur; 2007. Available from: http://www.pasteur.fr/fr/sante/centres-collaborateurs-l-oms-ccoms/salmon...
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and control (ECDC). The Surveillance Atlas of Infectious Diseases. Stockholm: ECDC. Available from: http://ecdc.europa.eu/en/data-tools/atlas/Pages/atlas.aspx
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

