Cinnamic Acid and Its Derivatives: Mechanisms for Prevention and Management of Diabetes and Its Complications
- PMID: 28230764
- PMCID: PMC5331594
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9020163
Cinnamic Acid and Its Derivatives: Mechanisms for Prevention and Management of Diabetes and Its Complications
Abstract
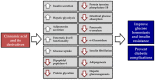
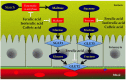
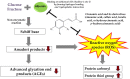
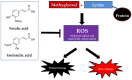
With recent insight into the development of dietary supplements and functional foods, search of effective phytochemical compounds and their mechanisms involved in prevention and management of diabetes and its complications are now being assessed. Cinnamic acid and its derivatives occur naturally in high levels of plant-based foods. Among various biological activities, cinnamic acid and its derivatives are associated with a beneficial influence on diabetes and its complications. The aim of the review is to summarize the potential mechanisms of these compounds for prevention and management of diabetes and its complications. Based on several in vitro studies and animal models, cinnamic acid and its derivatives act on different mechanism of actions, including stimulation of insulin secretion, improvement of pancreatic β-cell functionality, inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis, enhanced glucose uptake, increased insulin signaling pathway, delay of carbohydrate digestion and glucose absorption, and inhibition of protein glycation and insulin fibrillation. However, due to the limited intestinal absorption being a result of low bioavailability of cinnamic acid and its derivatives, current improvement efforts with entrapping into solid and liquid particles are highlighted. Further human clinical studies are needed to clarify the effects of cinnamic acid and its derivatives in diabetic patients.
Keywords: cinnamic acid and its derivatives; complications; diabetes; mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin-releasing properties of a series of cinnamic acid derivatives in vitro and in vivo.J Agric Food Chem. 2008 Sep 10;56(17):7838-44. doi: 10.1021/jf801208t. Epub 2008 Jul 24. J Agric Food Chem. 2008. PMID: 18651742
-
Butanol fraction of Parkia biglobosa (Jacq.) G. Don leaves enhance pancreatic β-cell functions, stimulates insulin secretion and ameliorates other type 2 diabetes-associated complications in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 May 13;183:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.02.018. Epub 2016 Feb 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26911526
-
Effects of cinnamic acid on complications of diabetes.Turk J Med Sci. 2018 Feb 23;48(1):168-177. doi: 10.3906/sag-1708-8. Turk J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29479980
-
Coumarins as potential antidiabetic agents.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;69(10):1253-1264. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12774. Epub 2017 Jul 3. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28675434 Review.
-
Aminoacid support in the prevention of diabetes and diabetic complications.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Feb;10(1):8-17. doi: 10.2174/138920309787315194. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19275668 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum metabolome and gut microbiome alterations are associated with low handgrip strength in older adults.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 1;16(3):2638-2656. doi: 10.18632/aging.205501. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38305839 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic Potential of Commonly Available Fruit Plants in Bangladesh: Updates on Prospective Phytochemicals and Their Reported MoAs.Molecules. 2022 Dec 8;27(24):8709. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248709. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cinnamic Acid Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Hepatic Lipogenesis and Promoting Fatty Acid Oxidation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 2;2021:9561613. doi: 10.1155/2021/9561613. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34512784 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory evaluation of Curculigo latifolia on α-glucosidase, DPP (IV) and in vitro studies in antidiabetic with molecular docking relevance to type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):109-121. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1844680. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33249946 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Nano Drug Delivery Systems for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Available Administration Strategy for Antidiabetic Phytocompounds.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Dec 16;15:10215-10240. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S285134. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33364755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

