Common Chemical Inductors of Replication Stress: Focus on Cell-Based Studies
- PMID: 28230817
- PMCID: PMC5372731
- DOI: 10.3390/biom7010019
Common Chemical Inductors of Replication Stress: Focus on Cell-Based Studies
Abstract
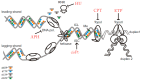
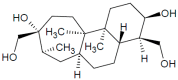
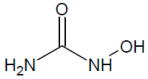
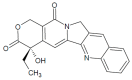
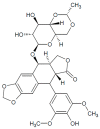
DNA replication is a highly demanding process regarding the energy and material supply and must be precisely regulated, involving multiple cellular feedbacks. The slowing down or stalling of DNA synthesis and/or replication forks is referred to as replication stress (RS). Owing to the complexity and requirements of replication, a plethora of factors may interfere and challenge the genome stability, cell survival or affect the whole organism. This review outlines chemical compounds that are known inducers of RS and commonly used in laboratory research. These compounds act on replication by direct interaction with DNA causing DNA crosslinks and bulky lesions (cisplatin), chemical interference with the metabolism of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (hydroxyurea), direct inhibition of the activity of replicative DNA polymerases (aphidicolin) and interference with enzymes dealing with topological DNA stress (camptothecin, etoposide). As a variety of mechanisms can induce RS, the responses of mammalian cells also vary. Here, we review the activity and mechanism of action of these compounds based on recent knowledge, accompanied by examples of induced phenotypes, cellular readouts and commonly used doses.
Keywords: replication stress; aphidicolin; camptothecin; cancer; cisplatin; etoposide; hydroxyurea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
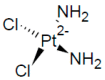
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

