Network neuroscience
- PMID: 28230844
- PMCID: PMC5485642
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4502
Network neuroscience
Abstract
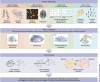
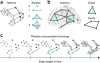
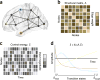
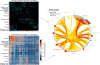
Despite substantial recent progress, our understanding of the principles and mechanisms underlying complex brain function and cognition remains incomplete. Network neuroscience proposes to tackle these enduring challenges. Approaching brain structure and function from an explicitly integrative perspective, network neuroscience pursues new ways to map, record, analyze and model the elements and interactions of neurobiological systems. Two parallel trends drive the approach: the availability of new empirical tools to create comprehensive maps and record dynamic patterns among molecules, neurons, brain areas and social systems; and the theoretical framework and computational tools of modern network science. The convergence of empirical and computational advances opens new frontiers of scientific inquiry, including network dynamics, manipulation and control of brain networks, and integration of network processes across spatiotemporal domains. We review emerging trends in network neuroscience and attempt to chart a path toward a better understanding of the brain as a multiscale networked system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
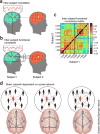
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

