RABiT-II: Implementation of a High-Throughput Micronucleus Biodosimetry Assay on Commercial Biotech Robotic Systems
- PMID: 28231025
- PMCID: PMC5525051
- DOI: 10.1667/RR011CC.1
RABiT-II: Implementation of a High-Throughput Micronucleus Biodosimetry Assay on Commercial Biotech Robotic Systems
Abstract
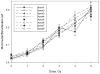
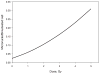
We demonstrate the use of high-throughput biodosimetry platforms based on commercial high-throughput/high-content screening robotic systems. The cytokinesis-block micronucleus (CBMN) assay, using only 20 μl whole blood from a fingerstick, was implemented on a PerkinElmer cell::explorer and General Electric IN Cell Analyzer 2000. On average 500 binucleated cells per sample were detected by our FluorQuantMN software. A calibration curve was generated in the radiation dose range up to 5.0 Gy using the data from 8 donors and 48,083 binucleated cells in total. The study described here demonstrates that high-throughput radiation biodosimetry is practical using current commercial high-throughput/high-content screening robotic systems, which can be readily programmed to perform and analyze robotics-optimized cytogenetic assays. Application to other commercial high-throughput/high-content screening systems beyond the ones used in this study is clearly practical. This approach will allow much wider access to high-throughput biodosimetric screening for large-scale radiological incidents than is currently available.
Figures





References
-
- Beinke C, Port M, Abend M. Automatic versus manual lymphocyte fixation: impact on dose estimation using the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2015;54:81–90. - PubMed
-
- Grace MB, Moyer BR, Prasher J, Cliffer KD, Ramakrishnan N, Kaminski J, et al. Rapid radiation dose assessment for radiological public health emergencies: roles of NIAID and BARDA. Health Phys. 2010;98:172–8. - PubMed
-
- Blakely WF, Carr Z, Chu MC, Dayal-Drager R, Fujimoto K, Hopmeir M, et al. WHO 1st consultation on the development of a global biodosimetry laboratories network for radiation emergencies (BioDoseNet) Rad Res. 2009;171:127–39. - PubMed
-
- IAEA Response Assistance Network Incident and Emergency Center: EPR-RANET Technical Document. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

