Differential regulation of C5a receptor 1 in innate immune cells during the allergic asthma effector phase
- PMID: 28231307
- PMCID: PMC5322932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172446
Differential regulation of C5a receptor 1 in innate immune cells during the allergic asthma effector phase
Abstract
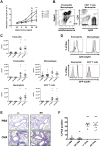
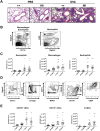
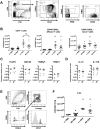
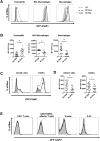
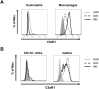
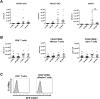
C5a drives airway constriction and inflammation during the effector phase of allergic asthma, mainly through the activation of C5a receptor 1 (C5aR1). Yet, C5aR1 expression on myeloid and lymphoid cells during the allergic effector phase is ill-defined. Recently, we generated and characterized a floxed green fluorescent protein (GFP)-C5aR1 knock-in mouse. Here, we used this reporter strain to monitor C5aR1 expression in airway, pulmonary and lymph node cells during the effector phase of OVA-driven allergic asthma. C5aR1 reporter and wildtype mice developed a similar allergic phenotype with comparable airway resistance, mucus production, eosinophilic/neutrophilic airway inflammation and Th2/Th17 cytokine production. During the allergic effector phase, C5aR1 expression increased in lung tissue eosinophils but decreased in airway and pulmonary macrophages as well as in pulmonary CD11b+ conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) and monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs). Surprisingly, expression in neutrophils was not affected. Of note, moDCs but not CD11b+ cDCs from mediastinal lymph nodes (mLN) expressed less C5aR1 than DCs residing in the lung after OVA challenge. Finally, neither CD103+ cDCs nor cells of the lymphoid lineage such as Th2 or Th17-differentiated CD4+ T cells, B cells or type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) expressed C5aR1 under allergic conditions. Our findings demonstrate a complex regulation pattern of C5aR1 in the airways, lung tissue and mLN of mice, suggesting that the C5a/C5aR1 axis controls airway constriction and inflammation through activation of myeloid cells in all three compartments in an experimental model of allergic asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The C5a/C5aR1 axis controls the development of experimental allergic asthma independent of LysM-expressing pulmonary immune cells.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 20;12(9):e0184956. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184956. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28931049 Free PMC article.
-
Allergen-Induced C5a/C5aR1 Axis Activation in Pulmonary CD11b+ cDCs Promotes Pulmonary Tolerance through Downregulation of CD40.Cells. 2020 Jan 26;9(2):300. doi: 10.3390/cells9020300. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31991941 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring and cell-specific deletion of C5aR1 using a novel floxed GFP-C5aR1 reporter knock-in mouse.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 15;194(4):1841-55. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401401. Epub 2015 Jan 14. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25589074
-
Anaphylatoxins coordinate innate and adaptive immune responses in allergic asthma.Semin Immunol. 2013 Feb;25(1):2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 19. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23694705 Review.
-
Differential effects of anaphylatoxin C5a on antigen presenting cells, roles for C5aR1 and C5aR2.Immunol Lett. 2019 May;209:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Immunol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30959077 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of Biliverdin Reductase A in Myeloid Cells Promotes Chemokine Expression and Chemotaxis in Part via a Complement C5a--C5aR1 Pathway.J Immunol. 2019 May 15;202(10):2982-2990. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701443. Epub 2019 Apr 5. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30952817 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and Interaction of Murine Pulmonary Phagocytes in the Naive and Allergic Lung.Front Immunol. 2018 May 16;9:1046. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01046. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29868009 Free PMC article.
-
C5a Blockade Increases Regulatory T Cell Numbers and Protects Against Microvascular Loss and Epithelial Damage in Mouse Airway Allografts.Front Immunol. 2018 May 24;9:1010. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01010. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29881374 Free PMC article.
-
Complement factor C5 inhibition reduces type 2 responses without affecting group 2 innate lymphoid cells in a house dust mite induced murine asthma model.Respir Res. 2019 Jul 24;20(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1136-5. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31340811 Free PMC article.
-
GM-CSF and IL-33 Orchestrate Polynucleation and Polyploidy of Resident Murine Alveolar Macrophages in a Murine Model of Allergic Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 11;21(20):7487. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207487. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maruo K, Akaike T, Ono T, Okamoto T, Maeda H. Generation of anaphylatoxins through proteolytic processing of C3 and C5 by house dust mite protease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;100:253–260. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

