Parkinson Sac Domain Mutation in Synaptojanin 1 Impairs Clathrin Uncoating at Synapses and Triggers Dystrophic Changes in Dopaminergic Axons
- PMID: 28231468
- PMCID: PMC5340420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.01.019
Parkinson Sac Domain Mutation in Synaptojanin 1 Impairs Clathrin Uncoating at Synapses and Triggers Dystrophic Changes in Dopaminergic Axons
Abstract
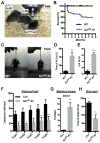
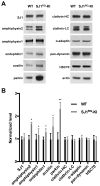
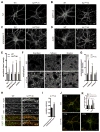
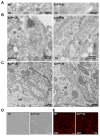
Synaptojanin 1 (SJ1) is a major presynaptic phosphatase that couples synaptic vesicle endocytosis to the dephosphorylation of PI(4,5)P2, a reaction needed for the shedding of endocytic factors from their membranes. While the role of SJ1's 5-phosphatase module in this process is well recognized, the contribution of its Sac phosphatase domain, whose preferred substrate is PI4P, remains unclear. Recently a homozygous mutation in its Sac domain was identified in early-onset parkinsonism patients. We show that mice carrying this mutation developed neurological manifestations similar to those of human patients. Synapses of these mice displayed endocytic defects and a striking accumulation of clathrin-coated intermediates, strongly implicating Sac domain's activity in endocytic protein dynamics. Mutant brains had elevated auxilin (PARK19) and parkin (PARK2) levels. Moreover, dystrophic axonal terminal changes were selectively observed in dopaminergic axons in the dorsal striatum. These results strengthen evidence for a link between synaptic endocytic dysfunction and Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: LRRK2; PARK19; PARK2; PARK20; PI(4,5)P2; Parkin; auxilin; neurodegeneration; nigrostriatal pathway; synaptic vesicle endocytosis; synaptojanin 1.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Parkinson disease and clathrin coat dynamics at synapses, why not?Mov Disord. 2017 Aug;32(8):1163. doi: 10.1002/mds.27097. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Mov Disord. 2017. PMID: 28681957 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arranz AM, Delbroek L, Van Kolen K, Guimaraes MR, Mandemakers W, Daneels G, Matta S, Calafate S, Shaban H, Baatsen P, et al. LRRK2 functions in synaptic vesicle endocytosis through a kinase-dependent mechanism. Journal of cell science. 2015;128:541–552. - PubMed
-
- Beilina A, Rudenko IN, Kaganovich A, Civiero L, Chau H, Kalia SK, Kalia LV, Lobbestael E, Chia R, Ndukwe K, et al. Unbiased screen for interactors of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 supports a common pathway for sporadic and familial Parkinson disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2014;111:2626–2631. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boassa D, Berlanga ML, Yang MA, Terada M, Hu J, Bushong EA, Hwang M, Masliah E, George JM, Ellisman MH. Mapping the subcellular distribution of alpha-synuclein in neurons using genetically encoded probes for correlated light and electron microscopy: implications for Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2013;33:2605–2615. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

