Downregulation of HuR Inhibits the Progression of Esophageal Cancer through Interleukin-18
- PMID: 28231690
- PMCID: PMC5784622
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.013
Downregulation of HuR Inhibits the Progression of Esophageal Cancer through Interleukin-18
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of human antigen R (HuR) downregulation and the potential target genes of HuR on the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Materials and methods: In this study, a proteomics assay was used to detect the expression of proteins after HuR downregulation, and a luciferase assay was used to detect the potential presence of a HuR binding site on the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of interleukin 18 (IL-18). In addition, colony formation assay, MTT, EdU incorporation assay, Western blot, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, transwell invasion assay, and wound healing assay were used.
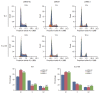
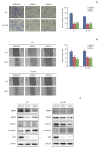
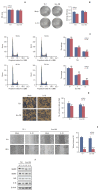
Results: In the present study, we found that the expression of both HuR protein and mRNA levels were higher in tumor tissues than in the adjacent tissues. HuR downregulation significantly suppressed cell proliferation. In addition, the metastasis of esophageal cancer cells was inhibited, while the expression of E-cadherin was increased and the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2, MMP9, and vimentin was decreased after HuR knockdown. Moreover, silencing of HuR disturbed the cell cycle of ESCC cells mainly by inducing G1 arrest. Furthermore, proteomics analysis showed that downregulation of HuR in TE-1 cells resulted in 100 upregulated and 122 downregulated proteins, including IL-18 as a significantly upregulated protein. The expression of IL-18 was inversely regulated by HuR. IL-18 expression was decreased in ESCC tissues, and exogenous IL-18 significantly inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of ESCC cells. The 3'-UTR of IL-18 harbored a HuR binding site, as shown by an in vitro luciferase assay.
Conclusion: HuR plays an important role in the progression of esophageal carcinoma by targeting IL-18, which may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Human antigen R (HuR); Interleukin-18; Neoplasm metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SEMA4D under the posttranscriptional regulation of HuR and miR-4319 boosts cancer progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21(2):122-129. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1669996. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31651222 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of SNHG1 suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by regulating Notch signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Dec 12;21(1):89-96. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170286. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 29081407
-
High MLL2 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression by inducing EMT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun;144(6):1025-1035. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2625-5. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29532228 Free PMC article.
-
Drug delivery approaches for HuR-targeted therapy for lung cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Jan;180:114068. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.114068. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 34822926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RNA-Binding Protein HuR in Digestive System Tumors.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 24;2020:9656051. doi: 10.1155/2020/9656051. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32775456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IFI35 is involved in the regulation of the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Jun 3;21(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01997-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34082779 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Pyroptotic Cell Death Pathways in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Sep 5;11(9):1313. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091313. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31492049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Novel Pyroptosis-Related Gene Signature Indicative of Disease Prognosis and Treatment Response in Skin Cutaneous Melanoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 12;15:6145-6163. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S367693. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35855761 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 in the tumor microenvironment is associated with the accumulation of FoxP3-positive regulatory T cells in human esophageal carcinomas.Virchows Arch. 2019 Nov;475(5):579-586. doi: 10.1007/s00428-019-02579-9. Epub 2019 May 6. Virchows Arch. 2019. PMID: 31062086
-
IRF1 regulates the progression of colorectal cancer via interferon‑induced proteins.Int J Mol Med. 2021 Jun;47(6):104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4937. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Int J Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33907823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K, Chang J, Wang Z, Li Y, et al. Genomewide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat Genet. 2012;44:1090–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

