Shared decision making PLUS - a cluster-randomized trial with inpatients suffering from schizophrenia (SDM-PLUS)
- PMID: 28231777
- PMCID: PMC5324213
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-017-1240-3
Shared decision making PLUS - a cluster-randomized trial with inpatients suffering from schizophrenia (SDM-PLUS)
Abstract
Background: Shared decision making (SDM) is a model of how doctors and patients interact with each other. It aims at changing the traditional power asymmetry between doctors and patients by strengthening the exchange of information and the decisional position of the patient. Although SDM is generally welcomed by mental health patients as well as by mental health professionals its implementation in routine care, especially in the more acute settings, is still lacking. SDM-PLUS has been developed as an approach that addresses both patients and mental health professionals and aims at implementing SDM even for the very acutely ill patients.
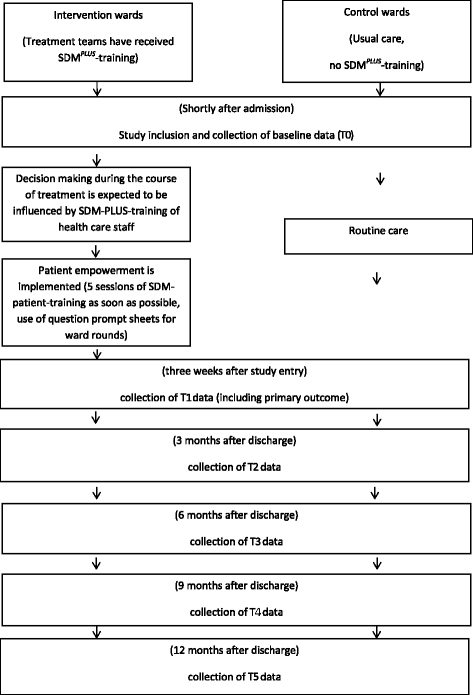
Methods: The SDM-PLUS study will be performed as a matched-pair cluster-randomized trial in acute psychiatric wards. On wards allocated to the intervention group personnel will receive communication training (addressing how to implement SDM for various scenarios) and patients will receive a group intervention addressing patient skills for SDM. Wards allocated to the control condition will continue treatment as usual. A total sample size of 276 patients suffering from schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder on 12 wards is planned. The main outcome parameter will be patients' perceived involvement in decision making during the inpatient stay measured with the SDM-Q-9 questionnaire. Secondary objectives include the therapeutic relationship and long term outcomes such as medication adherence and rehospitalization rates. In addition, process measures and qualitative data will be obtained to allow for the analysis of potential barriers and facilitators of SDM-PLUS. The primary analysis will be a comparison of SDM-Q-9 sum scores 3 weeks after study inclusion (or discharge, if earlier) between the intervention and control groups. To assess the effect of the intervention on this continuous primary outcome, a random effects linear regression model will be fitted with ward (cluster) as a random effect term and intervention group as a fixed effect.
Discussion: This will be the first trial examining the SDM-PLUS approach for patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder in very acute mental health inpatient settings. Within the trial a complex intervention will be implemented that addresses both patients and health care staff to yield maximum effects.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register DRKS00010880 . Registered 09 August 2016.
Keywords: Adherence; Schizophrenia; Shared decision making.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources