Allium hookeri root extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells
- PMID: 28231786
- PMCID: PMC5324216
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1633-3
Allium hookeri root extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Allium hookeri root extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Mar 28;17(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1709-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28351360 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Allium hookeri (AH) is widely consumed as a vegetable and herbal medicine in southeastern Asia. AH has been reported antioxidant, antimicrobial, improvement of bone health and antidiabetic effects. In the present study, we investigated the inhibitory effect of a methanol extract of AH root (AHE) on inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells.
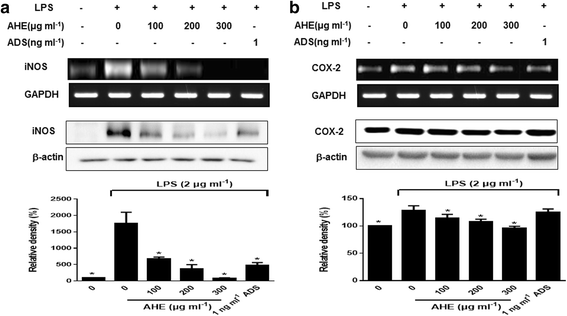
Methods: Initially, characterization of organic sulfur compounds in AHE was determined using high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS). Cells were incubated with LPS and AHE for 24 h. The productions of nitric oxide (NO), reactive oxygen species (ROS), and inflammation-related cytokines were examined. Gene and protein expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were assessed by polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting. Key factor, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) was also determined.
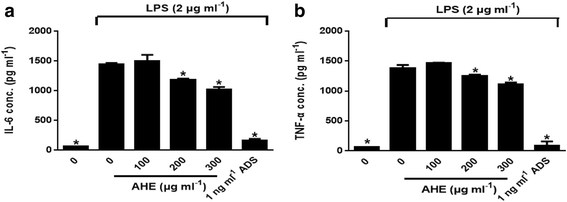
Results: AHE contained organosulfur compounds such as alliin and S-allylcysteine by HPLC-ESI-MS. AHE significantly inhibited NO, ROS, and cytokines production in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. In addition, AHE treatment inhibited iNOS and COX-2 mRNA and protein levels, leading to a decrease in iNOS-derived NO level. Furthermore, NF-κB activation was, at least in part, suppressed by AHE treatment.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that AHE treatment inhibits the inflammation condition through suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression via NF-κB down-regulation.
Keywords: Allium hookeri; COX-2; Inflammation; NF-κB; iNOS.
Figures




References
-
- Nicholas C, Batra S, Vargo MA, Voss OH, Gavrilin MA, Wewers MD, et al. Apigenin blocks lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality in vivo and proinflammatory cytokines expression by inactivating NF-kappaB through the suppression of p65 phosphorylation. J Immunol. 2007;179:7121–7127. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.7121. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

