Vildagliptin, but not glibenclamide, increases circulating endothelial progenitor cell number: a 12-month randomized controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 28231835
- PMCID: PMC5324295
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0503-0
Vildagliptin, but not glibenclamide, increases circulating endothelial progenitor cell number: a 12-month randomized controlled trial in patients with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Fewer circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and increased plasma (C-term) stromal cell-derived factor 1α (SDF-1α), a substrate of DPP-4, are biomarkers, and perhaps mediators, of cardiovascular risk and mortality. Short-term/acute treatment with DPP-4 inhibitors improve EPC bioavailability; however, long-term effects of DPP-4i on EPCs bioavailability/plasma (C-term) SDF-1α are unknown.
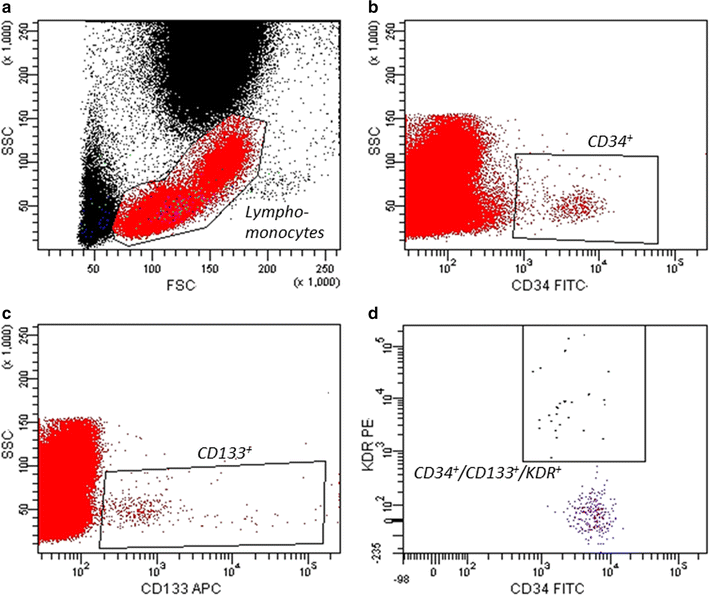
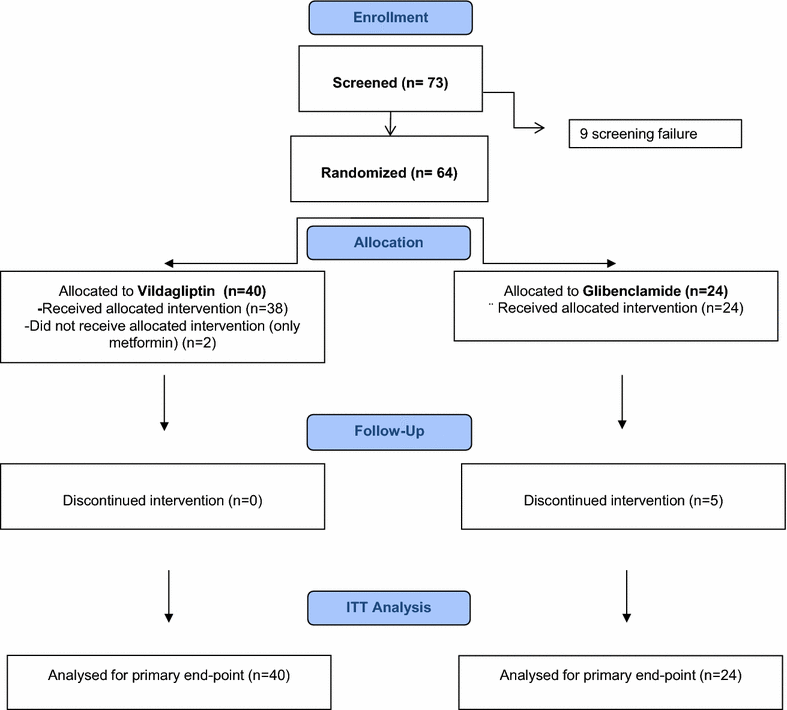
Methods: Randomized (2:1) open-label trial to compare the effects of vildagliptin (V) (100 mg/day) vs glibenclamide (G) (2.5 mg bid to a maximal dose of 5 mg bid) on circulating EPC levels at 4 and 12 months of treatment in 64 patients with type 2 diabetes in metformin failure. At baseline, and after 4 and 12 months, main clinical/biohumoral parameters, inflammatory biomarkers, concomitant therapies, EPC number (CD34+/CD133+/KDR+/106 cytometric events) and plasma (C-term) SDF-1α (R&D system) were assessed.
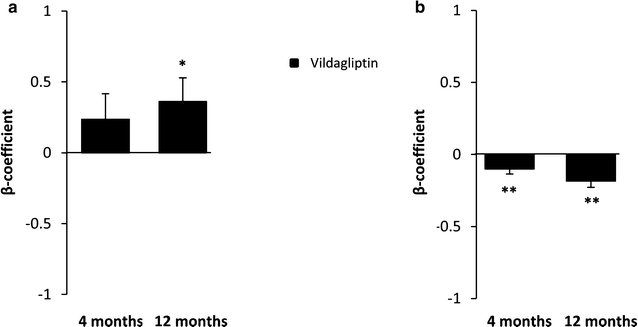
Results: Baseline characteristics were comparable in the two groups. V and G similarly and significantly (p < 0.0001) improved glucose control. At 12 months, V significantly increased EPC number (p < 0.05) and significantly reduced (C-term) SDF-1α plasma levels (p < 0.01) compared to G, with no differences in inflammatory biomarkers.
Conclusions: V exerts a long-term favorable effect on EPC and (C-term) SDF-1α levels at glucose equipoise, thereby implying a putative beneficial effect on vascular integrity. Trial registration Clinical Trials number: NCT01822548; name: Effect of Vildagliptin vs. Glibenclamide on Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cell Number Type 2 Diabetes. Registered 28 March, 2013.
Keywords: Cardiovascular risk; DPP-4 inhibitors; EPC; SDF-1α.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

